+1(209) 348-9544
order@myessayservices.com
+1(209) 348-9544
order@myessayservices.com
![]() Are you in High School, College, Masters, Bachelors or Ph.D and need someone to help in your homework? All you need is to ask for research paper help written by a specialist in your academic field. When you buy an essay online from My Essay Services, we offer you an original, nil plagiarized and unique paper written by a dedicated writer who is PhD or Masters qualified. MyEssayServices.com is an experienced service with over 9 years experience having delivered over 83,000 essays over the years.
Are you in High School, College, Masters, Bachelors or Ph.D and need someone to help in your homework? All you need is to ask for research paper help written by a specialist in your academic field. When you buy an essay online from My Essay Services, we offer you an original, nil plagiarized and unique paper written by a dedicated writer who is PhD or Masters qualified. MyEssayServices.com is an experienced service with over 9 years experience having delivered over 83,000 essays over the years.

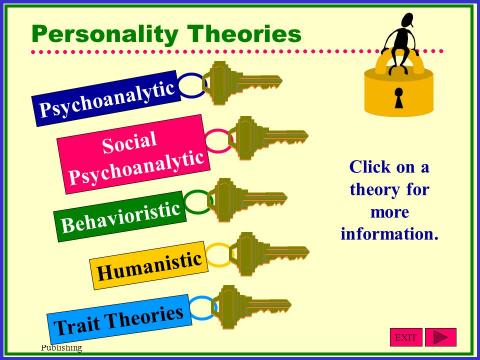 The majority use personality to allude to the most obvious traits in a person. Personality is behavior that manifests in the day-to-day activities of the majority of the people. However, this perception of personality is misleading given the fact that the personality entails more. In psychology, personality is concerned with the heredity and different outcomes in behavior. It explains why the people of the same heredity have different reactions to the same situation.
The majority use personality to allude to the most obvious traits in a person. Personality is behavior that manifests in the day-to-day activities of the majority of the people. However, this perception of personality is misleading given the fact that the personality entails more. In psychology, personality is concerned with the heredity and different outcomes in behavior. It explains why the people of the same heredity have different reactions to the same situation.
It explains why the people that are supposed to be similar owing to the nature and nurture environment display different perceptions and reaction to phenomena (Ellis, Abrams & Abrams, 2009). It is also used to look at the other side of the debate whereby, people that do not have any relationships have similar reactions to phenomena in their lives.
Study of personality entails the application of May idiographic and nomothetic techniques. The study of the personality entails the investigation of every aspect of the adult human behavior (Ellis, Abrams & Abrams, 2009). The personality studies have a focus on the adult behavior since the adults are more stable subjects to study since they have attained a level of little growth. The experience accrued by the adults from living also informed the decision to study personality using the adult subjects as opposed to the individuals.
Personality theories simulate new research findings, organize what is known and create formal perceptions of nature. There have been three groups of personality theories that have been advanced thus far (Ellis, Abrams & Abrams, 2009). The most common personality theories groups include trait, behavioral, psychoanalytic, and human learning. All the theories on personality state different attributions of behavior that persists in the lives of the individuals. They are optimizations of the real factors in life both of nature and nature that make the people behave according to a certain outline.
Human behavior, as explained from the different theoretical perspectives, does not mean that the outcomes of the analysis are the indicators of the real aspects that inform the human behavior (Ellis, Abrams & Abrams, 2009). Trait theory is one of the oldest theories that assert that the behavior or personality of a person is directly linked to the inherent traits in an individual. According to the theories, there is little that a person can do to influence his or her personality. Trait theories include phrenology, factor theory, and the typology (Fittskirk & Shohov, 2003).
Psychoanalytic theories are more modern given that they were established after advancement of theories such as traits theories (Fittskirk & Shohov, 2003). The psychoanalytic theories assume that there are two elements in the human nature that influence the outcome of the personality of the person. These two aspects of the psychic energy are the unconscious and the subconscious mind. The theory states that once a person has been awarded an identity, he or she will automatically develop the ego and superego. Ego and Superego form the structure of the personality. The personality theories advanced are based directly on the assertion of Sigmund Freud.
The learning theories were resultants of the attempts to express the psychoanalytic theory advanced by Freud in terms that could be subjected to the scientific rigor. Some of the advancements to the theory include the terming of the theories of human learning in terms of the cue and response (Ellis, Abrams & Abrams, 2009). The human behavior and personality are highly affected by the cue and the associated rewards.
The learning theories seek to link the learning and outcome of the people to the cues and the response that they will get (Fittskirk & Shohov, 2003). If a response is unwarranted, they learn to avoid the signal. If the cue is anticipated and more accurate, the human personality tends to align itself to the cues hence the development of a deeper understanding of the personality traits that may be erratic and contrary to the popular belief.
The learning theories occur in an individual context whereby if the context has the ability or trend of reinforcing a certain behavior, the people learn to adopt it and integrate it to the outcome. Therefore, the desirability of the outcome leads to the creation of the habit that is learned and assimilated in the learning theory. Improvements of the learning theories led to the creation of the learning theory in the conditioned environment.
The theory of operant conditioning assumes that the human behavior is a direct result of the condition (Fittskirk & Shohov, 2003). The assertion of operant conditioning implies that the human behavior is more so a result of the conditioned environment as opposed to the outcomes of the individual traits. The prevalence of a behavior is made possible through reinforcing the behavior, while a behavior that is not reinforced tends to be distinguished or weakened. The exposure of an individual led to the understanding of the conditions and the assimilation of the same in their learning behavior hence creation of a personality based on the conditioning (Ellis, Abrams & Abrams, 2009).
Further advancements of the theoretical findings of the previous researcher indicated that the human personality was a result of the interactions between the person and the environment. Albert Bandura asserted that the views of the self-efficacy and the environment led to the creation of the personality (Ellis, Abrams & Abrams, 2009). The theory seeks to explain the personality from the complex interaction of the above aspects. It also seeks to refute the exclusive nature that the other theories assumed when approaching the theoretical foundation creation.
Other important advancements in the theory of personality have been created such as the person-centered theory. Abraham Maslow focused on the wholeness of the persons more by empathizing on the importance of the needs in the creation and reinforcement of a certain behavior (Fittskirk & Shohov, 2003). Abraham Maslow’s assertions focused on hierarchal motivations of the behavior hence the outcome of a certain personality.
Other theories focus on the creation of the five factors that they purported to be central to the outcome of the human behavior and eventual development of the personality. The factors include the agreeableness the conscientiousness, the neuroticism, extraversion and openness that the person has to the experience (Fittskirk & Shohov, 2003). The above factors were mainly the major influencers of the decision of the person to take a certain course of action or not. More focus is not on the relationship between the person and the environment and the influence of the above relationship on the outcomes.
Before focusing on the in-depth analysis of the personality theories, it is important to understand personality from the different perspectives. Personality is the way that a person behaves, in short, the outcome of the human behavior. Personality is the main motivation of the human classification since it provides a chance for every individual to display a certain set of behaviors (Fittskirk & Shohov, 2003). Personality is the ability to aggregate different features that can be identified from different individuals and they work out for the individuals in a predetermined manner. Therefore, due to this reason, personality can be considered as an aggregate of human behavior (Ellis, Abrams & Abrams, 2009).
Personality in the second case is the way the person presents himself to the other people. The issue of definition led to the creation of the idea that the personality theories are contradictory (Ellis, Abrams & Abrams, 2009). The cause of the disagreement in terms of the personality can be seen as both present and absent. The theories of personality are mere indications of the different standpoints as far as the human personality is concerned. They are not concerned with the outcome of the personality per se. There are different ways of explaining the different personality as defined.
Theories of personality
The theories of personality are often categorized according to the human behavior and the dependency or relativity of the behavior in groups of different people. A trait is an enduring and a stable characteristic of human being (Fittskirk & Shohov, 2003). The traits are the aspects of human behavior that persist tot eh extent of increasing the accuracy level in the prediction of the reaction of the person to a certain scenario. Therefore, any change in behavior is indicative of a change in the traits of the person. The body features could be used to introduce certain aspects of the personality or make assumptions about the behavior of the person.
According to the human behaviorist, the aspects of a person’s physique could be sued to explain some of the humanistic traits that the person displays. The traits have been used to advance assertions such as the Napoleonic syndrome, which associates the human behavior to a certain body morphological aspect. The theories also assume that the traits can be overt and covert. The limited behavior of the individual is influenced by the underlying factors that may lead to a certain pervasive behavior (Berelson & Steiner, 1964).
The psychoanalytic theories of development emphasize on the relationship between unconscious impulses and overcoming conflicts. It can be used in the therapy as well as an explanation of the human behavior. The theory of psychoanalyzes assumes that the outcome of the personal traits depicted by any individual is related to the ability of the person to relate the past and the present. It assumes that the experiences of the persons will determine the outcome of the human behavior that he or she will depict in the end (Wade & Tavris, 2000).
The psychoanalytic theories identify the subconscious aspects that are influenced by the previous experiences of the person, and they affect the overt abilities to relate. Therefore, if the person had a certain experience that hindered or suppressed the expression of the trait, he or she may indicate a version behavior towards the trait.
The experience could be influenced or driven by external forces such as the parent reinforcing a certain trait in the child (Berelson & Steiner, 1964). It could also arise from the most overt experiences such as the treatment of another person who depicted given trait. The psychoanalytic theories postulate that the human behavior or the personality that one depicts is a direct outcome of the human experience.
The theory also assumes that the ego of the person has an impact on outcome of the personality of an individual. The people that have big egos have different personalities as opposed to the people that have personalities that are more erratic (Fittskirk & Shohov, 2003). Therefore, the human behavior is more or less of a depiction of the relationships between the subconscious mind which is by large affected by the previous experiences and the conscious mind which is affected by the present and more persistent aspects.
Modern theories of personality have more different emphasis contrary to the ones that the previous theories, the theories on social learning focus on the development of the personality according to the learning experiences (Berelson & Steiner, 1964). The previous theories approached character as an isolated matter that was distinct from the environment and social interactions. Social theories or learning theories of personality seek to refute the assumption that the human behavior is an isolated aspect.
They focus on the creation of the synthesis of the interactions between the environment and the person (Berelson & Steiner, 1964). They also focus on the interaction of the different people in the environment as the main influences of the personality (Myers, 2004). Social learning theories are, therefore, more accurate compared to the original theories.
The social learning theorists focused on the creation of scientific method on which they would investigate the assertions of the previous theories (Wade & Tavris, 2000). The scientific process was initially meant to subject the psychoanalytic theory into the rigor of scientific process in order to identify the replicability of the findings and the assertions in the different contexts. Social learning theorists also focused on the creation of a more in-depth understanding of the aspects that inform the human behavior.
The assertions were more focused on the observation of the behavior as opposed to the theorization of the different behavior (Berelson & Steiner, 1964). Therefore, the outcomes of the observed studies were more reliable compared to the outcomes of the mere theorization. The theories indicate that the human behavior or personality is also learned and not inherent as some of the original theories such as the traits theories postulated.
With the above assertions, the issue of the main determinant of the personality of person is still evident in the modern theories (O'Hagan, 2003). Some of the theories state that the outcome of person is mainly based on the heredity of the person. The assertion assumes that the outcome of a person could be affected by the genetic aspects. This is true since some of the traits indicated such as aggression have been suggested to be linked to the personality and the heredity. Therefore, some of the assertions of the trait theory are true (O'Hagan, 2003).
However, there are also assertions that the outcome of a person is mainly affected by the environment. The environment that a person is exposed to has a major bearing on the personality of the person (Myers, 2004). In most of the cases, whenever a person is incarcerated or placed in an environment that requires aggression survives. There is a high chance that the outcomes of the person will be affected by the environment.
Therefore, the environment is a major determinant of the eventual outcome of the individual. The environment determines the outcome of a person in terms of the ability to trust oneself. The self-efficacy is also a construct of the environment (Berelson & Steiner, 1964). In the event that a person has the environmental influences that assert that one has to behave in a particular manner for him or her to be considered worthy, the environmental impacts will result in the creation of open approach to the new influence such that the outcome will be in tandem with the environmental influences (Myers, 2004). Therefore, the theories of personality are accurate depending on the character being explored and extent of the exploration (O'Hagan, 2003).
References
Berelson, B., & Steiner, G. (1964). Human behavior. New York: Harcourt, Brace & World.
Ellis, A., Abrams, M., & Abrams, L. (2009). Personality theories. Los Angeles: SAGE Publications.
Fittskirk, P., & Shohov, S. (2003). Focus on behavioral psychology. New York: Nova Science Publishers.
Myers, D. (2004). Psychology. New York: Worth Publishers.
O'Hagan, A. (2003). Personality. Orlando: Harcourt.
Wade, C., & Tavris, C. (2000). Psychology. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
 Adlerian theory is a psychology therapy based on the theory of Alfred Adler. Alfred Adler was a historically influential psychiatrist and philosopher, born on 1870 and later on passed on in 1937. The idea of Adlerian theory is to focus on to focus on new ideas that were arising in the twentieth century. Adler in his theory focused on exploring factors like lifestyle, social interests, birth order, concepts relating to superiority and inferiority as the main principles of personality and parental education. Adler played a great role in the field of psychopathology, personality and psychotherapy. The main ideology of the theory is that an individual is more cooperative and responsive when they feel that they are encouraged or have feelings of respect and adequacy. However, when an individual is discouraged, they tend to produce counter-productive behaviors (Oberst & Stewart, 2003, 34). The behaviors normally consist a display of competition, and withdrawal after defeat. This essay deals with the strengths and weaknesses of the Adlerian theory.
Adlerian theory is a psychology therapy based on the theory of Alfred Adler. Alfred Adler was a historically influential psychiatrist and philosopher, born on 1870 and later on passed on in 1937. The idea of Adlerian theory is to focus on to focus on new ideas that were arising in the twentieth century. Adler in his theory focused on exploring factors like lifestyle, social interests, birth order, concepts relating to superiority and inferiority as the main principles of personality and parental education. Adler played a great role in the field of psychopathology, personality and psychotherapy. The main ideology of the theory is that an individual is more cooperative and responsive when they feel that they are encouraged or have feelings of respect and adequacy. However, when an individual is discouraged, they tend to produce counter-productive behaviors (Oberst & Stewart, 2003, 34). The behaviors normally consist a display of competition, and withdrawal after defeat. This essay deals with the strengths and weaknesses of the Adlerian theory.
Before analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of the Adlerian theory, it is important first to have clear knowledge of the facts associated with the theory. Adler started looking into the issues like parent education, equality, lifestyle, personality and influence of birth order in the early 1900’s. According to Adler, all humans have one basic goal and desire: to belong somewhere and feel important. In his books and lectures, written to the public, common sense according to Adler is a key component. According to Adler philosophy, an individual’s ability to adapt to feelings of insecurity, inferiority and inadequacy is key with relation to other people. A number of factors cause such emotions with one of them being birth order. Birth order refers to the order in which an individual is ranked according to their age and that of the siblings.
According to birth order, an individual may be the first-born, second born, third born or even a number past three according to the number of siblings. In the development and growth of children, the Adlerian theory proves to be of great significance. According to Adler, a misbehaving child happens to be discouraged child. Therefore, it is of importance to make a child feel encouraged, competent, valued and significant. Such strategies are of importance when it comes to understanding and living with children who possess difficult behaviors. On the issue of birth order also, a child may feel inferior due to their former humiliation in the family (Carlson & Maniacci, 2006, 45. The child may also feel inferior due to a physical condition or defect, or the lack of social feeling for others. Therefore, the type of parenting and homes in which children are brought up in plays a major role in their personality.
Parental education plays a major role in determining the kind of children a family brings up. Parents need to understand their children and bring them in a way that gives them encouragement to fight any feelings of inferiority. Children also create a personality emerging from the strategies, private and unique beliefs. Either the children themselves can pick out the beliefs or parents may inflict them on the children. Adlerian theory also emphasizes on the efforts individuals compensate for their inferiority, which is self-perceived to others. However, as the children grow, they have the power to change the change the beliefs they are formerly exposed to. As one matures, they have the power to evaluate their past life experiences and examine reoccurring behaviors in their past life. In doing this, one can identify beliefs and behaviors that helps an individual gain significance and belonging that growth, healing and change occur.
Family therapy, individual therapy and couples therapy is carried out according to Adlerian psychology. The focus of the psychologists is to tell the clients to release their unproductive feelings and their focus their attention towards more positive corrections. The positive corrections include behaviors, values and feelings that promote positive growth. Socratic dialogue is a key component of the Adlerian therapy that inspires the beneficial and productive attitudes (Oberst & Stewart, 2003, 144). The beneficial and productive attitudes involve areas of confidence and attitude. An individual’s ability to capitalize on the areas above increases their ability to form cohesive relationships and cooperate with others naturally. However, the Adlerian theory has its strengths and weaknesses just like any other theory. First, we will focus on the strengths then weaknesses of the Adlerian theory.
Adlerian theory is useful when it comes to solving people’s lifestyle problems. Adlerian therapy has the role of helping a client achieve a healthy and competitive life that is well rounded. The theories associated with Adlerian therapy happen to apply to all cultural groups, which is a great advantage. For example, the theme of encouragement and collaboration is traditionally emphasized for Hispanic and Asian groups. Sibling rivalry is another key component of Adlerian therapy and is common with traditional European North Americans. According to European North Americans, competitions are stressed out as a way of getting ahead. Adlerian therapy is also of great importance when it comes the treatment of specific disorders. A great number of disorders are found in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM), which is the standard classification of mental disorders (Adler, 2006, 99).
The disorders include conduct and antisocial disorders, personality disorders as well as anxiety related disorders. Counseling the Adlerian theory is also as an approach that can be used to help clients with psychology problems together with other theories. Adlerian theory is also of great importance when it comes to parents and guiding them in parenting. According to Adlerian theory, parents need to know how to bring up children in order to help them nurture their strengths and fight their weaknesses. The upbringing of a child very much determines their personality, behaviors and aspects towards life. Parents also need to understand that according to Adlerian theory; birth order plays a great role in a child behavior and attitude towards other people.
Through Adler theory, we can understand that humans relate to social relations in a great way compared to sexual urges. When it comes to inferiority, humans have the drive to overcome a sense of inferiority through striving for increasing higher levels of development (Corey, 2009, 99). Parents need to urge their children that they should not be a product of their genetics or environment. The parents should encourage their children that they have can interpret, create and influence events. According to Adler, genetics and environment should not limit an individual to use all the limitations and abilities they possess. Alder theory is also important when it comes to encouragement and motivation of individuals. The theory helps define encouragement, which is difficult to define, but simple to understand. Encouragement is very fundamental for helping teachers and parents to mold the relationships with the children.
The advantage is that it creates an atmosphere of democracy and cooperation in schools and the family. Adler emphasizes that encouragement is a fundamental attitude and should not be treated as a technique. Encouragement is defined as the process of offering courage to other individuals. Encouragement is spread through interactions with other individuals. It is important for adults to offer encouragement to children and the only way the can do this is by: proving to the children that they have significance even if the situation turns out poorly. Encouragement does not only work perfectly for child-adult relationships but also works out for relationships between spouses. A spouse can encourage his or her partner that their mere existence is the most important thing, and the rest of issues do not matter.
However, despite the identified strengths, the Alder theory also has some weaknesses. Adlerian therapy has not proven to have any effect in helping solving alcoholism. Earlier scholars and critics criticize the Adlerian theory for not being scientific (Adler, 2006, 78). The concepts brought up by the theory still have to stand up to scientific rigors of the laboratory. Other critics also claim that the concepts presented in the Adlerian theory are sexist in nature and simply wrong. A good example is sibling rivalry, which is a common thing in the West. However, according to the Adlerian theory, it is not advisable to encourage sibling rivalry since it may cause some of the children to feel inferior.
When it comes to Adlerian therapy, another disadvantage is the amount of information collected from a family. The information collected might end up exposing information about the family that the members would have preferred if it were kept secretive. The use of Adlerian therapy may also occur to be too long for managed care. A big number of individuals after therapy expect results after a short while (Carlson & Maniacci, 2006, 124). However, when Adlerian therapy happens to take too long, some of the clients may end up losing hope.
Adlerian therapy labels people rather than making diagnosis. Therefore, its effectiveness is questionable due to this limitation. Adlerian therapy works better on clients who are intelligent and highly-verbal. Therefore, this leaves out very many people from successfully receiving the therapy and appreciating its effect. For the therapists, it proves to be hard to interpret some aspects like dreams.
In conclusion, the Adlerian theory is of great significance when it comes to the day-to-day life of an individual. The Adlerian theory plays a role in forming good relationships between children and adults, between families and spouses. The use of the concepts in the Adlerian theory is core when it comes to children. One of the main advantages of the Adlerian theory is that it deals with fighting any feelings of inferiority. Adlerian theory also solves the problem of discouragement, which might lead to withdrawal (Rule and Bishop, 2006, 59).
The theory is also useful when it comes to psychotherapy and amending relationships between individuals. Encouragement according to the theory is fundamental to both children and adults in fighting any feeling of inadequacy or inferiority. The major teaching according to the Adlerian theory is that every individual tends to show more cooperation and responsiveness when they feel that they are encouraged or have feelings of respect and adequacy. However, when an individual is discouraged, they tend to produce counter-productive behaviors that show withdrawal.
References
Adler, A., Stein, H., & Alfred Adler Institute of Northwestern Washington. (2006). The general system of individual psychology: Overview and summary of classical Adlerian theory & current practice. Bellingham, WA: Classical Adlerian Translation Project.
Carlson, J., Watts, R. E., & Maniacci, M. (2006). Adlerian therapy: Theory and practice. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association. (Carlson & Maniacci, 2006, 124)
Corey, G. (2009). Theory and practice of counseling and psychotherapy. Belmont, CA: Brooks/Cole.
Oberst, U. E., Stewart, A. E. (2003). Adlerian Psychotherapy: An Advanced Approach to Individual Psychology. New York, USA: Psychology Press.
Rule, W. R., Bishop, M. (2006). Adlerian Lifestyle Counseling: Practice and Research. London, UK: Taylor & Francis
Personality is usually made up of characteristics pattern of thoughts, behaviors, and feelings that differentiates a person from the rest and makes them unique. These traits arise from within the individual and remain purely constant throughout an individual’s life. It is usually the compilation of a person’s traits in terms of compassion, emotions, believes among others.
The bio psychosocial theory was developed by a psychologist known as Erick Erikson. He believed that personality develops in a certain series of stages that describes the impact social experience plays across a person’s whole lifespan. It is in this sense that Erikson analyzed the dimensions in bio- psychosocial development (Erikson, 2008). They are:
1. Trust versus Mistrust stage (0-1 year)
This is the initial stage in the development. In this stage, the child develops the trust in the environment and world at large, given that the child’s experience is consistent and has continuity and similarity. The child at this stage is depending on the parent or guardian who happens to be the caregiver. The child should be given utmost care and attended on consistently in a bid to gain trust.
2. Autonomy versus Shame and Doubt (2-3 years)
Autonomy is an act of executing freedom. A child at this stage should have an absolute freedom to do what they please at their own space. The mother and caregiver are advised not to do everything for the child as self- doubt may occur in the process. A child should be given all they need to learn and become independent.
3. Initiative versus Guilt (3-5 years)
Restriction of self- initiative and the failure of a caregiver from answering questions poised by a child may lead to guilt consciousness in the child. Children try to initiate things that they feel it matters to their caregiver. For example, they sketch a drawing and try to show their caregiver in a bid to feel appreciated
4. Industry versus inferiority
At this stage, children have started growing mentally and join schools. Skills learnt in school become vital in the sense that it drives a child’s life’s work. For instance, the children become responsible for the homework given in school. They develop a sense of awareness in that they believe every work can be established industry or they won’t succeed.
5. Identity versus Role confusion (12-18 years)
A child at this stage comes to the end of a childhood stage and enters the teenager phase. Adolescent is now visible in a youth, as they grow concern on intentions they portray to others. Erikson refers to this stage as the “physiological revolution”. For instance, a youth gains great sense of the clothes they wear, where they live among others.
6. Intimacy versus Isolation (young adulthood)
This stage is achievable only if people have developed a sense of identity and are extremely comfortable with it. Intimate relationship with others entails development of love and commitment, which can either be sexual or non- sexual. For instance, the youth start dating and having sex with their peers of the opposite sex.
7. Generatively versus Stagnation (middle age)
This is the stage where the aspect of selflessness and taking care of interested parties come to play. A generative person tends to enjoy family and work, while a stagnation person, cares less about others and more about themselves. For instance, people get married at this stage of life.
8. Integrity versus Despair (old age)
This is the last stage of life where human beings begin reflecting back at their achievement in life. They gain a sense of either despair or satisfaction in the reflection. For instance, most people tend to gauge their achievements based on their level of wealth, fame or power.
Cultural competence is generally the ability to effectively interact with other human beings that come from different cultures, economic, and social backgrounds. This particularly applies in the context of organization’s human resource. Diversity on the other hand is viewed as a balance between prevalence and value. They are major components in an organization’s well- being.
Cultural competence and diversity is built on four purely cognitive components. They are awareness, attitude, knowledge and skills. Awareness is seen as the relationship between a person’s reactions to people who tend to be different. Attitude in equal sense is based on the cultural biasness and beliefs in general. Knowledge on the other hand is the measure between consistency of our behaviors and our beliefs and values on equality. The last aspect is skills, which focuses mainly on practicing to perfection the cultural competence (Mizrahi & Mayden, 2001).
General systems theory is described as elements which are bounded and are in exchange. This revolves around the virtual effects of seeing, hearing, feeling or having a particular sense. General systems theory influences social order in the sense that self- reliance opens a lee- way to skills and competence. This revolves about decision making on the social aspect while in power, that is widely influenced by the elements of general systems. This elaborates on the cognitive relationship between general systems theory and social order (Friedman & Allen, 2005).
References
Erikson, E. (2008). Psychosocial Stages. Development Psychology, 1-3.
Friedman, B., & Allen, K. (2005). Systems Theory. Frameworks for Clinical Practice, 6-12.
Mizrahi, T., & Mayden, R. (2001). Cultural Competence. National Association of Social Workers, 3-11.
Personality traits refer to the tendency of a person or manager to think, act of reason in a particular way based on hi/her personality. The personality of a manager has great influence on his/her way of reasoning, approaching problems as well as dealing with people. While some managers are could be demanding, difficult to get along with and critical of other people, other are positive and easily bond with other people. Both the appreciative and critical manager can yield great results in an organization although they influence employees differently (Chapter, 2014). This paper focuses on locus of control as a personality trait among managers.
People have different perceptions towards the things that happen around them. While some think that their fate is already defined and cannot be changed, others believe that they can alter their fate by doing certain things. Locus of control is defined as the manager’s perception towards how much control he/she has over the surrounding circumstances. The locus of personality can be divided into two; internal and external locus of control.
Under internal locus of control, the manager believes that he/she is responsible over his/her fate (Chapter, 2014). For such a manager, it is the actions that a person does that determine his success. Such mangers insist on perfection and expect their employees to give their best in every task. They are always willing to put more effort towards implementing certain policies since they believe that putting more effort yields greater results.
On the other hand, external locus of control defines a manager who thinks that outside forces define his fate (Chapter, 2014). Such a manager, there are some methods that bring ultimate success while others are bound to fail. A manager with the external locus of control personality trait is a bit reluctant to trying new techniques since he/she thinks that there are other forces that determine the outcome of something.
References
Chapter 3. (2014). Values, attitudes, emotions and culture: the manager as a person. JPG File.
Browse More Essay Topics 24/7/365 Support 11+ Yrs in Essay Writing Pay for Quality not Quantity Score that A+ Grade
Affordable Papers
Research Paper for Sale
Cheap Research Papers
Buy Term Papers
Buy Research Paper
Write My Paper
Buy an Essay
Cheap Essay Writer
Write my Essay
Thesis Help
Dissertation Help
Paper Writing Service
Pay for Homework
Pay for Research Paper
Do My Essay for Me
Pay for Essay
College Papers for Sale
Do My Homework for Me
College Essays for Sale
Buy Research Papers Online
Buy College paper
Client: "(Berlin, G.K., CA)"
Topic title:"Leadership shortfalls in Blue Chips"
Discipline: "Economics"
Pages: 5, (APA)
" Awesome, the writer delivered it as required by the professor. They also sent me a plagiarism & grammar report Wow!. I was worried about how the essay would turn up but this is exactly what wanted. Thank you and will be back with a longer essay"
Accounting Research Papers
Business Research Papers
Communication Research Papers
Computer Science Research Papers
Economic Research Papers
Film Studies Research Papers
Finance Research Papers
Geography Research Papers
History Essays
Psychology Research Papers
Political Science Research Papers
Nursing Research Papers
Mathematics Essays
Management Essays
Literature Essays
Law Essays
World Affairs Essays
Technology Essays
Sociology Essays
Science Essays
Religion Essays
+1(209) 348-9544
Terms
Privacy
Sitemap
Frequently Asked Questions
0% Plagiarism Guarantee
Money Back Guarantee
Revision Policy
