+1(209) 348-9544
order@myessayservices.com
+1(209) 348-9544
order@myessayservices.com
![]() Every academic student understands clearly how challenging it can be to meet a tight deadline. Once you are short of time, and the task should be done within some timelag, you may end up asking yourself: “Is there anyone who can help me write a custom essay online?” That’s where My Essay Services.com can be your perfect choice. Whether your a PhD, Masters, College High School or Bachelors we can deliver an original paper as per your instructions.
Every academic student understands clearly how challenging it can be to meet a tight deadline. Once you are short of time, and the task should be done within some timelag, you may end up asking yourself: “Is there anyone who can help me write a custom essay online?” That’s where My Essay Services.com can be your perfect choice. Whether your a PhD, Masters, College High School or Bachelors we can deliver an original paper as per your instructions.
When you buy an essay online from us, we offer you an original, nil plagiarized and unique paper written by a dedicated writer who is PhD or Masters qualified. My Essay Services is an experienced service with over 9 years experience having delivered over 83,000 essays over the years.


 Deficiency in vitamin B12 and folic acid contributes to megaloblastic anemia, a condition where the red blood cells are larger than their normal. Megaloblastic anemia manifests with symptoms such as hyperactive reflexes, ataxia and peripheral neuropathy among others. Both folate and vitamin B12 play a crucial role in DNA synthesis (Olson, 2012). Replacement therapy has been used to treat deficiency of vitamin B12 and folic acid. This can be done both orally and intravenously. It should have been appropriate to mention dietary supplements that are rich in both vitamin B12 and folate. Furthermore, there is not mention of the role of vitamin B12 and folate in cellular metabolism.
Deficiency in vitamin B12 and folic acid contributes to megaloblastic anemia, a condition where the red blood cells are larger than their normal. Megaloblastic anemia manifests with symptoms such as hyperactive reflexes, ataxia and peripheral neuropathy among others. Both folate and vitamin B12 play a crucial role in DNA synthesis (Olson, 2012). Replacement therapy has been used to treat deficiency of vitamin B12 and folic acid. This can be done both orally and intravenously. It should have been appropriate to mention dietary supplements that are rich in both vitamin B12 and folate. Furthermore, there is not mention of the role of vitamin B12 and folate in cellular metabolism.
Response 2
Anemia that arises from the deficiency of folic acid and Vitamin B12 is known as macrocytic/megaloblastic (Katzung, Masters, & Trevor, 2012). In addition, both vitamins play a crucial role in DNA synthesis. Dietary vitamin B12 needs to be converted to its active form to enable effective utilization. It would have been a sufficient explanation of the pathway that converts vitamin B12 to the active form. Folic acid exists in both active and inactive form (Katzung, Masters, & Trevor, 2012). Dietary measures form the main approach of treating folic acid deficiency. Example of food that is rich in both vitamin B12 and folate include legumes, whole grain and fresh green vegetables. Oral supplementations, IM and subcutaneous injection of cyanocobalamin help in treating Vitamin B12 deficiency. Intranasal variants are available for individuals who cannot tolerate the two approaches.
Response 3
Excellent work done but it would have been better to distinguish the mechanism of action between aspirin, heparin and warfarin as primary anticoagulants. Aspirin as an NSAID is administered to prevent platelet aggregation. It has inhibitory effects on cyclooxygenase in both platelets and endothelial cells. Heparin prevents formation of new clots with no effect on the existing one. Warfarin acts by blocking vitamin K binding sites. It acts on existing clots thus preventing their extension (Katzung, Masters, & Trevor, 2012). Clopidogrel is a drug that helps in preventing stroke. It is administered with warfarin to prevent ischemia and unstable angina. The major side effect of warfarin is internal bleeding. It may also cause birth defects and abortion, therefore, not appropriate for use by pregnant women. Furthermore, there is no mention of the side effects associated with the medications.
Response 4
Aspirin has an inhibitory effect on COX. Clinical use of aspirin helps to treat transient ischemic attacks, MI and thrombosis. Aspirin is also used as a pain reliever due to its anti-inflammatory action by inhibiting prostaglandins
 Prothrombin depends on vitamin k as a cofactor. It is activated by Xa to make thrombin. Thrombin in turn converts fibrinogen to fibrin, which stimulates blood clotting. Prothrombin has a plasma half-life of 60 hours (Bick, 2009).
Prothrombin depends on vitamin k as a cofactor. It is activated by Xa to make thrombin. Thrombin in turn converts fibrinogen to fibrin, which stimulates blood clotting. Prothrombin has a plasma half-life of 60 hours (Bick, 2009).
Can vitamin B1 deficiency cause memory issues?
Vitamin B1 is a complex vitamin, which helps strengthen the body’s immune system and tolerate stressful conditions. Deficiency of vitamin B1 causes fatigue, abdominal discomfort and irritability. Moreover, deficiency of this vitamin also allows pyruvic acid to form in the bloodstream. This causes a reduction in the level of mental alertness, which can in turn lead to memory loss (Devanand, 2011).
Can vitamin 12 deficiency cause depression?
Vitamin B-12 plays a vital role in maintaining the level of brain chemicals that affect most brain functions. Low levels of the vitamin can lead to depression on the patient. Low levels of the vitamin are caused by inability of one’s body to consume vitamins and poor diet (Devenand, 2011).
Can vitamin B-12 deficiency cause fatigue?
Vitamin B-12, also known as cobalamin, plays a key role in making DNA and keeping red blood cells and nerve cells healthy. Vitamin B-12 has been known to reduce fatigue, high cholesterol levels and Alxheimer’s disease. The deficiency of the vitamin is mostly linked to old age, and lack of the enough vitamin levels cause fatigue on the patient (Devenand, 2011).
What foods mandated by laws is folic acid added in?
Folic acid was banned from all food processing methods after it was discovered that it can lead to neural tube defects in mothers. However, continued research showed that folic acid can reduce the dangers of Alzheimer’s disease and it also has some protective effects on various types of cancers. This followed a lawful restriction that flour manufacturers should use certain levels of folic acid. Thus, flour is the only food mandated by the law to fortify folic acid restrictions (Preedy, Srirajaskanthan & Patel, 2013).
How often is a patient INR monitored when warfarin is started?
All warfarin patients require INR monitoring. The danger of bleeding while on warfarin is high among patients who have not previously received warfarin. INR is monitored in the first three months of the warfarin treatment to avoid the INR from exceeding 3.0. After the first three months, the monitoring period can be reduced according to the physician’s assessments on the patient (Handin, Lux & Stossel, 2010).
References
Bick, R. L. (2009). Disorders of thrombosis and hemostasis: Clinical and laboratory practice. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Devanand, D. P. (2011). The Memory Program: How to Prevent Memory Loss and Enhance Memory Power. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Preedy, V. R., Srirajaskanthan, R., & Patel, V. B. (2013). Handbook of food fortification and health: From concepts to public health applications. New York, NY: Humana Press.
Handin, R. I., Lux, S. E., & Stossel, T. P. (2010). Blood: Principles and practice of hematology. Philadelphia, Pa: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
 Sickle Cell Anemia is a body disorder that entails sickle-shaped red blood cells. Normal red blood cells assume the shape of s disc. This enables normal red blood cells to move through blood vessels. Moreover, normal red blood cells have iron a rich protein known as hemoglobin. This protein facilitates transportation of oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body.
Sickle Cell Anemia is a body disorder that entails sickle-shaped red blood cells. Normal red blood cells assume the shape of s disc. This enables normal red blood cells to move through blood vessels. Moreover, normal red blood cells have iron a rich protein known as hemoglobin. This protein facilitates transportation of oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body.
The thesis of this essay is to evaluate the epidemiology, disease etiology, pathological changes and clinical manifestations of sickle cell anemia. Moreover, this essay assesses the available disease management plans available for sickle cell anemia patients.
Sickle cells present in sickle cell anemia patients contain abnormal hemoglobin (hemoglobin S). Sickle hemoglobin causes the red blood cells become sickle shaped. Sickle cells are often sticky and stiff. They hinder the blood flow in blood vessels present in the organs and limbs. Further, blocked blood flow causes organ damage and pain on the patient. Consequently, blocked blood flow also raises the risk for infection. Patients with sickle cell anemia have lower numbers of red blood cells compared to normal people (Bjorklund, 2011).
Red blood cells are secreted in the spongy marrow, which are located in the larger bones in the body. The bone marrow produces new red blood cells to replace replenished red blood cells. Normal red blood cells have a life span of relatively 120 days in the blood stream. They facilitate transportation of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide from the body. For patients with sickle cell anemia, the abnormal sickle cells are replenished after 10-20 days. The bone marrow cannot reproduce other red blood cell to replace the replenished ones fast enough. Therefore, the bloodstream contains fewer red blood cells, which limit the transportation of oxygen in the body (Forget, Higgs, Steinberg & Weatherall, 2009).
Abnormal hemoglobin S can lead to complications such as high mortality and morbidity. Normal hemoglobin molecules present in blood cells transport oxygen from lungs to other body organs. However, Hemoglobin S causes disruption in the body gaseous exchange. Unlike normal red blood cells, sickle cell anemia disrupts the normal shape of red blood cells and this lead to rigidity. The rigidity of the red blood cells limits the penetration of the cells in blood vessels. Thus, the clog together and cause blockages that limit transportation of oxygen to other body parts and removal of carbon dioxide (Forget, Higgs, Steinberg & Weatherall, 2009).
In the United States, sickle cell disorder is one of the most prevalent single gene disorders. The disease affects about 72000 people and estimated 2million carriers annually in United States. In addition, abnormal cells are less mobile compared to normal shaped cells. Further, these abnormal cells can cause blockage of blood vessels. This can result in organ and tissue damage leading to sever pains. These pains are called ‘sickle cell crisis’ and they may last for a long time (Bjorklund, 2011).
Causes of sickle cell anemia
Sickle cell disorder is caused by gene mutation. The gene mutation occurs when there is alteration in the genes that make hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is necessary for efficient transportation of oxygen from the lungs to other body parts. Patients with sickle cell anemia have abnormal hemoglobin that lead to stickiness and rigidity of the red blood cells. Sickle cell anemia is caused by a gene mutation that is inherited. The gene is autosomal, not linked to any sex chromosome, recessive in nature. Thus, the gene is passed from the parent carrier to the children (Ricci & Kyle, 2009).
However, for the sickle cell anemia gene to manifest, it must be passed from both parents as carriers. Therefore, if both the parents are carriers, the child gets two sickle cell genes that can manifest in the sickle cell disorder. The inheritance of a single sickle cell makes the child a carrier. However, the disease will not present in the carrier. The carriers of the sickle cell gene do not need any hospitalizations and their life expectancy levels are similar to that of normal people. However, symptoms or complications can manifest in high altitudes where there is less oxygen. An advantage for sickle cell carriers is that they are less prevalent to malaria. This is because the deformed red blood cells hinder the development of malaria. If both parents have sickle cell anemia, the chances of their children getting the sickle cell condition are one in four (Forget, Higgs, Steinberg & Weatherall, 2009).
Clinical Manifestations of Sickle Cell Anemia
Signs and symptoms of patients with sickle cell anemia manifest early during childhood. Many patients present with chronic and acute pain in most body parts. Sickle cell disease manifests mostly in vaso-occlusive crisis. Pain crises are the most prevalent distinguishing features of sickle cell anemia. Consequently, bone pains are also common for patients with sickle cell disease. The long bones induce most of the pain due to the infarction of the bone marrow. Anemia is not bound to any geographic location and it affects people of all origin. The disease can lead to major complications such as aplastic crisis, which is a serious complication resulting from infection with B19V (Forget, Higgs, Steinberg & Weatherall, 2009).
Moreover, splenic sequestration presents during the onset of chronic anemia that can cause rapid enlargement of the spleen. Furthermore, it can lead to high reticulocyte count. For patients with sickle cell disease, the condition can lead to deadly infections that pose great danger to the patient. For instance, respiratory bacteria such as streptococcus pneumonia are more prevalent in sickle cell anemia patients.
Sickle cell disease can also need to growth retardation and delayed sexual maturation. This presents in adolescence and childhood stages. Growth retardation in adolescents triggered by sickle cell disorder in associated with decreased Hb concentration and increase in the level of energy consumption.
Hand-foot syndrome also presents in sickle cell anemia patients. Hand foot syndrome presents with dactylitis, a condition which inflicts bilateral pain and swollen hands or feet in young children. Dactylitis condition occurs between 6 months to 3 years of an infant. However, the condition disappears after 5 years due to hematopoiesis; small bones present in the feet and hands ceases after five years. Destruction of the metatarsal and metacarpal bones appears on radiographs after 3-5 weeks from when the swelling begins (Bjorklund, 2011).
Consequently, sickle cell anemia patients may also experience acute chest syndrome. For example, little children experience chest pains, coughs, fevers, pulmonary infiltrates, tachypnea and leukocytosis. On the other hand, adults experience conditions such as dyspneic with chest pains, afebrile and lower lobe infection. Patients with sickle cell anemia risk developing an acute respiratory distress syndrome. In children cases, acute chest syndrome can occur due to infection. Moreover, fat embolism and pulmonary infarction may occur triggered by bone marrow infarction (White, Duncan & Baumle, 2011).
In addition, sickle cell anemia also presents with pulmonary hypertension. This is a serious complication of the disease and it can lead to death. Pulmonary hypertension occurs because blood in the pulmonary circulation becomes deoxygenated. This results to a high degree of polymer formation. For patients with the disorder, lungs develop areas of microthrombi and microinfarction, which hinder the blood flow. The areas that lack oxygenation lead to the sickling process. Thus, the pulmonary hypertension occurs (Fishman, Ballantyne, Rathmell & Bonica, 2010).
The disease also causes vascular acclusion that leads to avascular necrosis of the humeral or femoral head. The central nervous system is also affected by sickle cell anemia. Alteration of the central nervous system can lead to severe complications such as stroke. Further, ophthalmologic involvement of the body is also altered by the Hemoglobin S condition. The disease triggers ptosis, proliferative retinitis and retinal vascular changes. The disease also affects the cardiac involvement in major body functions such as dilation of the left atrium and ventricles (White, Duncan & Baumle, 2011).
Consequently, in some situations, the disease presents with cholelithiasis in children. In addition, the liver in children can be affected by the cholelithiasis condition. Moreover, sickle cell anemia affects the body kidneys making them lose concentration capacity. Thus, the disorder causes priapism complication. The disorder also affects the dermatologic involvement of the body. This can lead to leg ulcers, which cause chronic pain. The sickle cell disorder also presents with vaso-occulsive crisis. These crises include hypoxemia, which occurs because of respiratory complications and acute chest syndrome (Ricci & Kyle, 2009).
Dehydration also occurs because of the disorder. Dehydration occurs because of acidiosis. Acidiosis is a condition that triggers a shift of the oxygen dissociation curve. Occasionally, the disorder presents with changes in body temperature. Leg ulcers cause chronic pain for patients with the sickle cell disease. Leg ulcers occur because of minor injury to the area surrounding the malleoli. Poor circulation characterized by microinfarcts and sickling trigger slowed healing. Moreover, poor circulation of blood can also lead to prevalence of other infections.
Treatment implications of the disease
Patients with sickle cell disorder start presenting with the symptoms 5months after birth. However, the symptoms for sickle cell disorder differ among patients, with some having mid symptoms and others severe symptoms. Infants do not present any symptoms during birth because the fetal hemoglobin protects the baby’s red blood cells from sickling. Nevertheless, the fetal hemoglobin is replaced by sickling hemoglobin five months after birth. Diagnosis of sickle cell anemia is not limited to any single disease management plan (White, Duncan & Baumle, 2011).
Hand and Foot Syndrome
The first symptoms of the sickle cell disorder are swelling in the feet and hands. Swellings are accompanied with fever are among the first symptoms to present. Swellings are caused by clogging of the sickle cells in the blood vessels, thus blocking the flow of blood to the feet and hands. Swellings in the feet and hands can be treated by pain medicine. Further, clinicians will increase fluids in the patient’s body, by adding fluids such as water (Forger, Higgs, Steinberg & Weatherall, 2009).
Management of Pain Crisis
Pain crises are some of the most prevalent symptoms of sickle cell disorder. The pain is caused when sickle cells clog in the blood vessels preventing blood flow. The pain level varies among patients with some reported mild or severe cases. The pain can last for any length of time depending on the condition of the patient.
Prevention of pain crises can be improved by engaging in healthy practices. These healthy practices include, drinking a lot of water to increase the levels of body fluids. Moreover, patients are also advised to avoid extreme temperatures. These include too cold or too hot environments (Sinatra, 2009).
In addition, patients should avoid being exposed to high altitudes. For instance, flying and mountain climbing are disapproved for patients with the disorder. Consequently, the patients should avoid becoming exposed to low oxygen levels. Adults presenting with severe sickle cell disorder are prescribed to a medicine called hydroxyurea. Hydroxyurea reduces the level of pain crises experienced by the patients. Nevertheless, the drug should not be taken without the doctor’s prescription. This is because the drug can cause adverse effects on the patient. Pain crises encountered by sickle cell disorder patients can also be treated using over the counter prescriptions such as aspirin and ibuprofen. Patients with severe pain are given opioid prescriptions such as morphine. In case of emergencies, patients may be admitted for intense treatment (Ricci & Kyle, 2009).
Patients with sickle cell disorder experience various physical conditions that cause body distress. Sickle cell disorder leads to depletion of red blood cells frequently. Thus, the body frequently experiences situations where the red blood cells fail to transport enough oxygen to the body and removal of carbon dioxide from the body. This leads to various physical conditions such as tiredness, fast heart rate, dizziness, pale skin, irritability, delayed puberty, jaundice and slow growth. The treatment option for these physical conditions includes blood transfusion. Blood transfusion is done when patients encounter severe anemia. Severe anemia occurs because of enlargement of the spleen or infection (Bjorklund, 2011).
However, blood transfusion can cause health complications on the patient because of the iron content present in the blood. Further, hemosideorsis, iron overload, can lead to liver, pancreas and heart damage. Thus, this can lead to other infections such as diabetes mellitus. Iron chelation therapy is performed for patients receiving regular blood transfusions to avoid excess iron levels (Sinatra, 2009).
Infection Management
Sickle cells disorder patients, mostly infants and young children, are at the risk of developing infections. These patients are prevalent to capsules bacteria, which target the spleen. Moreover, children with the disorder are also prevalent to pneumonia that may cause death. Therefore, prevention measures should be put in place to reduce the prevalence of these diseases. Infections can be prevented by administering vaccines (Fishman, Ballantyne, Rathmell, Bonica, 2010).
Vaccines protect the body against harmful infections. For instance, adults with the disorder can receive annual flu vaccines accompanied by meningococcal and pneumococcal vaccine. Further, other vaccines can be administered according to doctor’s indications. Treatment for infections includes treatment with antibiotic medicines and blood transfusion. Patients are advised to report any symptoms when they start presenting in order to pave way for early diagnosis of the condition (Fishman, Ballantyne, Rathmell & Bonica, 2010).
Acute Chest Syndrome
 Acute chest syndrome can lead to life threatening situations. Hence, the condition should receive immediate clinical attention. Signs and symptoms should be reduced to stable conditions. Prevention of this condition includes drug prescription. Hydroxyurea helps patients prevent acute chest symptoms. However, patients taking hydroxyurea should receive keen monitoring from health practitioners. This is because the medicine can lead to negative adverse effects that may lead to further complication of the disorder. Post surgery patients can use incentive spirometer to prevent acute chest syndrome. Treatment of the condition entails administering oxygen and medicine to treat infections. Medicines are administered to open the airways. Further, medicines are prescribed to improve the effect of blood transfusion for patients (Sinatra, 2009).
Acute chest syndrome can lead to life threatening situations. Hence, the condition should receive immediate clinical attention. Signs and symptoms should be reduced to stable conditions. Prevention of this condition includes drug prescription. Hydroxyurea helps patients prevent acute chest symptoms. However, patients taking hydroxyurea should receive keen monitoring from health practitioners. This is because the medicine can lead to negative adverse effects that may lead to further complication of the disorder. Post surgery patients can use incentive spirometer to prevent acute chest syndrome. Treatment of the condition entails administering oxygen and medicine to treat infections. Medicines are administered to open the airways. Further, medicines are prescribed to improve the effect of blood transfusion for patients (Sinatra, 2009).
Splenic Sequestration
Splenic sequestration is a dangerous condition and medical intervention should be done in hospital. Splenic sequestration occurs when a large amount of sickle cells get stuck in the spleen. Thus, they cause the spleen to enlarge. This causes various symptoms such as sudden weakness, fast breathing, abdominal pain, pale lips, extreme thirst and fast breathing. Parents who have a child with the sickle cell disorder should learn how to monitor the spleen’s size and report any changes in the spleen size (Bjorklund, 2011).
Patients with severe or life threatening splenic sequestration should receive regular blood transfusions. Moreover, the spleen can be removed in a surgery referred as splenectomy. Splenectomy is done to prevent splenic sequestration from reoccurring. Treatment options for the condition include blood transfusion. Blood specialists should be involved in the blood transfusion. Blood specialists help in enhancing normal flow of blood when blood trapped in the spleen is released. The release of this blood can lead to a fluid overload in the body. Thus, removal of blood can be necessary to avoid this situation (Ricci & Kyle, 2009).
Vision Loss
Vision loss can lead to blindness for sickle cell disorder patients. Vision loss occurs when blood vessels present in the eye are blocked by the sickle cells and the retina is damaged. Extra blood vessels may develop in the eye because of lack of oxygen. Prevention of the condition entails eye checkups annually. Eye check-ups should be performed by eye specialists, who have specialized on retina diseases. The treatment options include laser treatment in cases where the retina becomes damaged by excessive blood vessel growth. Laser treatment prevents further vision loss (Ricci & Kyle, 2009).
Leg Ulcers
Led ulcers mostly affect the lower parts of the leg. Leg ulcers are more prevalent on males than females. The symptoms present from 10 to 50 years after birth. Leg ulcer formation are caused by a combination of various factors such as infection, inflammation, trauma and disruption of blood circulation in the smallest blood vessels present in the leg. Treatment for leg ulcers includes ointments and medicated creams. Leg ulcers cause pain and patients are given pain relievers. Furthermore, leg ulcers is managed by use of cultured skin grafts. Cultured skin grafts are provided in specialized centers (White, Duncan & Baumle, 2011).
Stroke
Stroke results from clogging of the sickle cells anemia in the blood vessels, leading to blockage of blood flow to the brain. Relatively 10% of children who suffer from sickle cell disorder develop asymptomatic stroke. This stroke can lead to lifelong disabilities and learning problems. Prevention of the stroke condition can be done through transcranial Doppler ultrasound (TCD). Transcranial Doppler ultrasound is performed to detect the risk of developing stroke in children. Children found prevalent to developing stroke condition, are recommended to frequent blood transfusions. Blood transfusions can help prevent stroke in children (Ricci & Kyle, 2009).
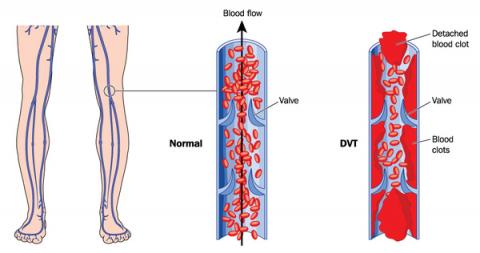
Pulmonary Embolism (PE) and Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Increasing risk of blood clot is induced by sickling of the red blood cells. Clogging of the deep vein (DVT) or clogging in the lung (pulmonary embolism) can cause serious illness and disability. In extreme cases, it can lead to mortality. Prevention and treatment measures include prescription of effective medications. Further, immediate medical intervention should occur when the first symptoms present (White, Duncan & Baumle, 2011).
Sickle cell anemia is still a major health threat that can lead to mortality. There are no specific treatments for the sickle cell disorder. However, there are emerging issues ongoing to increase the disorder prevention and management measures. For instance, stem cell transplant has been achieved to replace the bone marrow for sickle cell patients with bone marrow from a healthy donor. However, there are inefficiencies resulting from this procedure and this can lead to further complications (Bjorklund, 2011).
Reference
Bjorklund, R. (2011). Sickle cell anemia. New York: Marshall Cavendish Benchmark.
White, L., Duncan, G., & Baumle, W. (2011). Foundations of Adult Health Nursing. Clifton Park, N.Y: Delmar/ Cengage Learning.
Ricci, S. S., & Kyle, T. (2009). Maternity and pediatric nursing. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Fishman, S., Ballantyne, J., Rathmell, J. P., & Bonica, J. J. (2010). Bonica's management of pain. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins.
Sinatra, R. S. (2009). Acute pain management. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Forget, B. G., Higgs, D. R., Steinberg, M. H., & Weatherall, D. J. (2009). Disorders of Hemoglobin: Genetics, Pathophysiology, and Clinical Management. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Browse More Essay Topics 24/7/365 Support 11+ Yrs in Essay Writing Pay for Quality not Quantity Score that A+ Grade
Affordable Papers
Research Paper for Sale
Cheap Research Papers
Buy Term Papers
Buy Research Paper
Write My Paper
Buy an Essay
Cheap Essay Writer
Write my Essay
Thesis Help
Dissertation Help
Paper Writing Service
Pay for Homework
Pay for Research Paper
Do My Essay for Me
Pay for Essay
College Papers for Sale
Do My Homework for Me
College Essays for Sale
Buy Research Papers Online
Buy College paper
Client: "(Berlin, G.K., CA)"
Topic title:"Leadership shortfalls in Blue Chips"
Discipline: "Economics"
Pages: 5, (APA)
" Awesome, the writer delivered it as required by the professor. They also sent me a plagiarism & grammar report Wow!. I was worried about how the essay would turn up but this is exactly what wanted. Thank you and will be back with a longer essay"
Accounting Research Papers
Business Research Papers
Communication Research Papers
Computer Science Research Papers
Economic Research Papers
Film Studies Research Papers
Finance Research Papers
Geography Research Papers
History Essays
Psychology Research Papers
Political Science Research Papers
Nursing Research Papers
Mathematics Essays
Management Essays
Literature Essays
Law Essays
World Affairs Essays
Technology Essays
Sociology Essays
Science Essays
Religion Essays
+1(209) 348-9544
Terms
Privacy
Sitemap
Frequently Asked Questions
0% Plagiarism Guarantee
Money Back Guarantee
Revision Policy
