+1(209) 348-9544
order@myessayservices.com
+1(209) 348-9544
order@myessayservices.com
![]() Are you in High School, College, Masters, Bachelors or Ph.D and need someone to help in your homework? All you need is to ask for research paper help written by a specialist in your academic field. When you buy an essay online from My Essay Services, we offer you an original, nil plagiarized and unique paper written by a dedicated writer who is PhD or Masters qualified. MyEssayServices.com is an experienced service with over 9 years experience having delivered over 83,000 essays over the years.
Are you in High School, College, Masters, Bachelors or Ph.D and need someone to help in your homework? All you need is to ask for research paper help written by a specialist in your academic field. When you buy an essay online from My Essay Services, we offer you an original, nil plagiarized and unique paper written by a dedicated writer who is PhD or Masters qualified. MyEssayServices.com is an experienced service with over 9 years experience having delivered over 83,000 essays over the years.

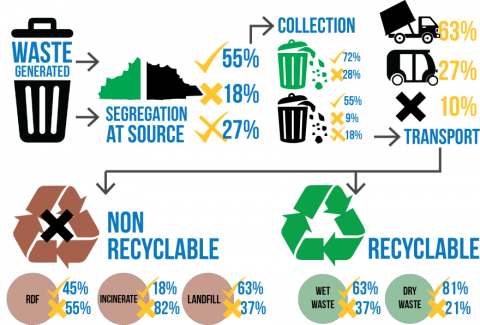 The issue of waste is a common problem that affects all the people. All people produce wastes from their activities. Households produce waste in the form of household rubbish. The larger the population, the more the waste that it generates. On addition to the household waste, the industrial processes, construction and water cleaning activities contribute to the total waste generated in the region (Pomberger & Ragossnig, 2014). The approach adopted in dealing with the wastes determines the extent of the environmental degradation that will come from the wastes.
The issue of waste is a common problem that affects all the people. All people produce wastes from their activities. Households produce waste in the form of household rubbish. The larger the population, the more the waste that it generates. On addition to the household waste, the industrial processes, construction and water cleaning activities contribute to the total waste generated in the region (Pomberger & Ragossnig, 2014). The approach adopted in dealing with the wastes determines the extent of the environmental degradation that will come from the wastes.
Organic waste eventually decomposes. This might seem to be the solution to the organic waste management. However, the process of decomposition leads to the emission of greenhouse gasses. The greenhouse gasses contribute to the rise in global warming. Waste disposal also leads to loss of material that could have been used in the generation of other material. Some of the raw materials used in the making of the waste components are imported, and the government has to incur additional costs in buying the material back.
The type and amount of wastes are increasing. The nature of the waste disposed of is also changing due to the different products needed (Pomberger & Ragossnig, 2014). For instance, the dramatic rise in the use of telecommunication materials has led to the breeding of a new kind of waste. The changes in technology have rendered some of the products that were previously used redundant such that they have to be treated as waste. As a result, the nature of the wastes that the community currently generates is different from the nature of the waste that it previously contributed. The ways generated today is both complex and versatile.
Wastes produced could be hazardous to the people. Therefore, the management of the waste is important. Due to the magnitude of the risk posed by piling wastes, the producers of the commodities ought to come up with a direct and succinct plan aimed at the management of the wastes that result from the use of their products (Cherian & Jacob, 2012).
Companies ought to come up with policies that are aimed at the reduction of the health and environmental impacts of wastes that arise from their processes and products. They should also focus on the increment of the resource use efficiency. The long-term goal of the organization ought to be turning into a green-powered organization. The organization ought to focus on ways that it can use to ensure that it recycles some of the wastes from its previous operations.
It should also focus on the use of the unavoidable waste as another resource if it is possible (Cherian & Jacob, 2012). The attainment of these goals will ensure that it reduces the need for the extraction of the natural resources. The adoptions of proper waste management policies is a sure way of ensuring that the organization attains resource efficiency and sustainable growth.
Regardless of the appointed approach towards waste management, the process comes at a cost to the organization and the environment. The first step in waste management entails the collection of the waste from the source, taken to a sorting center and transported to the recycling center.
The processes mentioned above are often expensive and difficult to handle for the organization. The treatment process also leads to the release of greenhouse gasses (Pomberger & Ragossnig, 2014). Another major challenge is that the bulk of waste that an organization produces is toxic since it contains the heavy metals and other substances that may make the waste difficult to treat since there are special processes that are needed to treat the specific toxic matter in the waste.
Reduction of the quantities of the toxic matter used in the production of the material is advisable where possible (Gutberlet, 2010). In the event, that the company cannot remove the waste material entirely, it can come up with recycling processes that are configured to deal with the specific toxic matter. The organization is between suited to understand the nature of the materials that it uses in the production process. Coming up with the accurate ways of dealing with the waste is important since it increases the chances of the company being a green company. Green production can be a platform to launch into some markets.
Waste management ought to be a long-term strategy that is aimed at the creation of the blueprint according to which the organization manages wastes. Waste management ought to be modernized to meet the demands of the class of wastes. It should be managed in the most effective manner since the waste management policy leads determines the effectiveness of the management policy (Cherian & Jacob, 2012).
A paradigm shift in the thinking about waste management ought to be developed. The organization ought to focus on the waste and view it in a different manner. Instead of looking at waste as a burden, the organization ought to look at it as a resource that it can tap into. The waste can be reduced and reused or recycled. The approach used in dealing with the waste ought to be determined by the nature of the waste (Gutberlet, 2010). Companies in the construction industry can reuse over 70% of their waste. The municipal council can recycle 50% of the assorted wastes.
Adoption of a life approach
All products and services produced by any company have an effect on the environment. The impacts start from the process of extraction of the raw materials to manufacture, supply use and scrapping. The impacts on the environment assume the various forms of energy used, resource used and other kinds of pollutions that are involved in the process of production a certain output (Pomberger & Ragossnig, 2014).
The life cycle approach to waste management entails thinking of the entire process and identifying the individual set of wastes that are manifested in each of the stages in the life cycle. One has to look at all aspects of the production system and identify the areas that have the potential for improvement.
 The wastes identified in the process help in the reduction of the wastes of resources and the environment impact of wasting the resources. Reduction of the impacts of the wastes ought to be reduced and not pushed to the other stages in the production cycle. Wastes in manufacturing account for the additional costs of the product (Gutberlet, 2010). A wasteful production system leads to the development of additional costs that will be recovered in the price of the output. The wastes ought to be reduced in each stage of the product life cycle.
The wastes identified in the process help in the reduction of the wastes of resources and the environment impact of wasting the resources. Reduction of the impacts of the wastes ought to be reduced and not pushed to the other stages in the production cycle. Wastes in manufacturing account for the additional costs of the product (Gutberlet, 2010). A wasteful production system leads to the development of additional costs that will be recovered in the price of the output. The wastes ought to be reduced in each stage of the product life cycle.
The product life cycle stage that has the largest waste ought to be used as the basis of the determination of whether the product has to be replaced. For example, in the case of a washing machine, the largest amount of wastes that it generates is at the user stage. Therefore, the owner ought to replace it at this stage to reduce the amount of wastes that it generates, even though, the machine will end up being scrapped (Cherian & Jacob, 2012).
Therefore, the understanding of the process of waste management and the best practices depends on the process approach. The manufacturer ought to offer advice on the most vulnerable state in the production process at this stage since the advice will help the users in the determination of the best way of using the equipment and when to replace.
In some cases, some products cannot be recycled; these products have to be disposed of in the best way possible. One of the oldest ways of dealing with the unrecyclable products is to dispose of them off in the landfills. The landfill is one of the oldest ways of dealing with the wastes. However, it is the least desirable option given the adverse effects that it has on the environment. The landfills have the potential of producing and later releasing potent methane gas, which leads to the increase of the global warming (Gutberlet, 2010).
Methane is a more powerful greenhouse gas compared to carbon dioxide. Therefore, the production of this gas leads to the increase of the risk posed to the environment by the development of landfills. In some cases, methane build-ups can arise in the landfills leading to explosions. Additionally, the decomposition of the biodegradable material can lead to the development of leachate that could contaminate ground and surface water sourced leading to the development of public health issues.
However, despite the explicit issues that the landfills pose to the public health, some wastes can only be managed using the approach. Therefore, the company has to come up with the accurate landfill design approach to ensure that the adverse effects emanating from this approach do not materialize (Cherian & Jacob, 2012). Compliance with the standards on the design of the landfills is important since it determines the effectiveness of the model of waste disposal. The materials send to the landfills are mainly the biodegradable materials. If they were used in the production of compost manure, they could fetch the recyclers millions. Therefore, there is no waste that cannot be used to the production something that can be used to produce something of a greater value (Gutberlet, 2010).
Another way of handling waste is by converting it into energy through a system known as modern waste incineration. Modern incinerators can be used in the production of electricity and heating for the buildings. Some of the wastes could be used in fueling some of the industrial operations. However, poor burning of the material could result in the damage of the environment and expose the people to adverse health effects (Gutberlet, 2010). In order for the waste products to burn completely, the incinerators have to burn the waste under controlled environment.
Whenever, the process cannot guarantee that there will be no emission of the harmful products, additional measures ought to be undertaken to ensure that the harmful gasses are not released into the environment. Reduction of the gaseous release into the environment takes a second stage of incineration known as co-incineration. The design of the incineration plants has to consider the costs and the benefits.
A cost-benefits analysis ought to indicate that the outcome of buying and installing an incinerator is higher than the actual costs. The method is not the most efficient way of managing the waste materials since some of the waste materials release chemicals at higher temperatures. Therefore, incineration of wastes has to be take up as the last resort.
Companies have to focus on making the most out of their biowastes. The garden kitchen and food waste are the main components of the food thrown out of the homes, restaurants and workplaces. The majority of the biowaste goes into the landfills. However, dumping the waste in the landfills is not the most efficient way of handling the biowastes (Gutberlet, 2010). Biowaste has the potential of providing energy and compost manure. The bio-wastes can be put in the biogas digesters to trap the methane gas that is produced during the process of decomposition.
Recycling
 Most of the waste, that the common person throws away can be recycled and used to make another product. Recycling is the use of the waste materials to make another product or products of use. The process helps in the reduction of the wastes that end up in the dumpsites. Recycling is particularly important if the materials used to make the waste are imported.
Most of the waste, that the common person throws away can be recycled and used to make another product. Recycling is the use of the waste materials to make another product or products of use. The process helps in the reduction of the wastes that end up in the dumpsites. Recycling is particularly important if the materials used to make the waste are imported.
Dumping the waste as opposed to recycling means that the government and the companies that make the product will have to incur additional costs in buying the raw materials most of which they could have avoided (Cherian & Jacob, 2012). The recycled material will provide the factories with the essential raw materials such as the plastics, paper, glass and other metals.
Recycling is particularly important in the recovery of the precious metals used in the production of the electronics. Effective recovery of these components increases the chances of the company saving the costs that it would otherwise have incurred in buying the components directly from the suppliers (Gutberlet, 2010). The other advantage of recycling is that it helps in the reduction of energy used in the manufacture of a new product. For instance, recycling a can use 5% of the energy used to make a new can right from the processing of the raw materials.
The positive aspect of recycling is that it can be applied in different scenarios. The company dealing in construction could recycle some of the debris from the site and use them in the making of new bricks for the next stage in the construction or another site. The debris is particularly useful given that they already have some cement in them. Recycling could also be applied to the old vehicles (Cherian & Jacob, 2012). The mass of steel used in the manufacture of the new vehicles could be used for the development of the construction steel or be reused in the making of other body panels for the new vehicles.
Recycling is the responsibility of all people. Individuals have the role of ensuring that they adhere to the set procedures of recycling some products by sorting their wastes according to the set standards. The producers have the responsibility of marking all their products according to whether they are recyclable or not. Marking of the containers ought to be conspicuous and understood by all people (Cherian & Jacob, 2012). Use of the conventional signs determines the effectiveness of the process of recycling the wastes.
The producer’s responsibility can also be extended to indicate the time when the products turn into waste. The producer should be financially responsible if their products become wastes. The financial liability extended to the producers will give them the incentive to develop products that are environmentally friendly. They will also be encouraged to follow up on their products and scrap it themselves (Gutberlet, 2010).
References
Cherian, J., & Jacob, J. (2012). Management Models of Municipal Solid Waste: A Review Focusing on Socio Economic Factors. International Journal Of Economics And Finance, 4(10).
Gutberlet, J. (2010). Waste, poverty and recycling. Waste Management, 30(2), 171-173.
Pomberger, R., & Ragossnig, A. (2014). Future waste - waste future. Waste Management & Research, 32(2), 89-90
Abstract
 In the years that followed major nuclear accidents such as the Chernobyl disaster in the year 1986, nuclear power fell out of favor with many countries. In fact, most countries applied brakes to their programs. However, despite the Fukushima disaster that occurred in Japan, there has been a sort of renaissance in nuclear energy. The renaissance can be attributed to climate change, air pollution and growing demand for electricity all around the world. This is the reason as to why the governments continue to reconsider their repugnance to nuclear energy. Nuclear energy often emits little carbon dioxide and it has been able to build an impressive reliability as well as safety record. There are countries such as Japan that have completely reverse their different phase outs for nuclear power and other countries have extended the lifetimes of existing reactors. There have also been several countries that have developed plans for new nuclear plants despite the several disasters that have called into question the safety of the nuclear plants. However, Germany heeded the call by Fukushima and it decided that it was time to wind up its nuclear power plants. Germany therefore has decided to ensure that all its nuclear plants are phased out by the year 2022 because of security concerns. They have decided to take the reins in Europe and lead by example against what they describe as a dangerous source of energy. This paper is going to analyze why different countries in the world continue to use nuclear energy despite the fact that there have been several major nuclear disasters that have tainted the safety of the plants.
In the years that followed major nuclear accidents such as the Chernobyl disaster in the year 1986, nuclear power fell out of favor with many countries. In fact, most countries applied brakes to their programs. However, despite the Fukushima disaster that occurred in Japan, there has been a sort of renaissance in nuclear energy. The renaissance can be attributed to climate change, air pollution and growing demand for electricity all around the world. This is the reason as to why the governments continue to reconsider their repugnance to nuclear energy. Nuclear energy often emits little carbon dioxide and it has been able to build an impressive reliability as well as safety record. There are countries such as Japan that have completely reverse their different phase outs for nuclear power and other countries have extended the lifetimes of existing reactors. There have also been several countries that have developed plans for new nuclear plants despite the several disasters that have called into question the safety of the nuclear plants. However, Germany heeded the call by Fukushima and it decided that it was time to wind up its nuclear power plants. Germany therefore has decided to ensure that all its nuclear plants are phased out by the year 2022 because of security concerns. They have decided to take the reins in Europe and lead by example against what they describe as a dangerous source of energy. This paper is going to analyze why different countries in the world continue to use nuclear energy despite the fact that there have been several major nuclear disasters that have tainted the safety of the plants.
The principal risks that are associated with nuclear power often arise from health effects of radiation. The radiation often consists of subatomic particles that travel near the velocity of light at around 186,000 miles per second. These particles can penetrate deep into the skin of the human body and consequently damage the existing biological cells and in most cases they can initiate cancer. The nuclear power technology often produces materials that emit radiation and consequently they are referred to as being radioactive. In October 2011, a major disaster occurred in Japan that has changed the way many countries view nuclear Energy. The Fukushima disaster triggered the nuclear power plant in Japan. Three reactors were damaged which released radiation that were only a few times less than that which was experienced at Chernobyl. It is this disaster that caused widespread doubts in regards to the safety of nuclear power. It is at this time that countries such as Germany decided to announce their accelerated shutdown of their nuclear power programs.
Many Governments did not heed the Fukushima call to abandon their nuclear power and its benefit. Some of the developing countries have argued that electricity generation often emits more carbon dioxide as compared to nuclear power which can in fact be described as the largest source of carbon electricity in the United States. The fact that nuclear power generation is often relatively cheap in terms of maintenance and fuel makes it as an attractive deal for developing countries. In fact, it is of importance to understand that even after Fukushima disaster, countries such as China, Russia, India and South Korea still continue to expand their nuclear power plants and they show no push for backing out.
Literature Review
An article by the Japan Times News argues that developing countries have decided to embrace nuclear energy despite Fukushima woes. Japan closed down all its nuclear plants after the Fukushima metal down, detailing safety measures. However, despite this disaster many developing countries are leading a construction boom of nuclear power plants in more than two decades. It is of the essence to understand to understand that there are more than 70 reactors that are being constructed worldwide. According to the article, the construction is ongoing in China, India and other countries in the Asia-Pacific region. Power is needed in economies to grow and therefore, most countries have been put between a rock and hard place in that they have to consider their needs of electricity.
According to an article that was published in DW named 'Scrapping nuclear plants to cost billions', the article gives information regarding what will cost for Germany to shut down their nuclear plants. The article states categorically that the decision to move away from nuclear energy in Germany can be described as a done deal. The country intends to phase out all nuclear power plants by the year 2022. Despite this being a political decision that will undoubtedly cost billions of Euros, the government is determined to see through this project. There are several consequences that will be as a result of this shut down of the nuclear power. Firstly, energy will increase and this will push up electricity rates. According to the article, this is already a reality in Germany and electricity rates are already increasing. The decision on the shut-down on the nuclear reactors came on the wake of the Fukushima disaster that occurred in Japan.
Stefan Nicola in her article 'Renewable take top share of German power supply in First', she argues that for the first time the nation was able to get more renewable sources of energy despite the weaning nuclear power in the nation. Clean energy in the country has increased an in fact; the country intends to increase its renewable energy to around 50% in the year 2050. This efforts have been plagued by what can be described as runaway household prices, surge in coal use, rising pollution in the country and the over-reliance of natural gas from Russia.
According to an article by DW titled 'China's nuclear boom leaves Germany' argues that the decision that Germany took in order to phase-out nuclear energy has left the country isolated worldwide. China on the other hand as well as other handful countries has decided to ignore the warnings by Germany and have continued with their expansion regarding atomic energy. In fact, even Japan has which was hit by the Fukushima disaster has been able to return to its nuclear industry. The article argues that despite Japanese people not trusting nuclear energy any longer, they cannot be able to accept the high energy prices that have existed since the atomic-phase out. In fact, in its argument the Japanese government justified its decision to switch on its reactors back again by stating that high cost of electricity from other sources was crippling the Japanese economy.
In an article that appeared on the world nuclear news named 'Barakah 1 reactor vessel delivered' the article describes the arrival of a reactor vessel which is the initial unit of United Arab Emirates first nuclear plant that was delivered to a nuclear power plant construction site at Barakah. The UAE is developing country and consequently this article shows that indeed even developing countries have decided to embrace the new concept of nuclear power and this is the reason as to why they are building nuclear power plants.
Roy Broomby in his article argues that the Fukushima disaster led many countries to rethink their nuclear energy. He argues that there are countries such as Germany who have decided to abandon the nuclear energy program altogether. Instead of phasing out the nuclear energy completely the French government has decided to reduce its dependence to nuclear energy by a third in the next 20 years. According to the article, this can be described as a big risk to a country that currently relies on around 75% of electricity on nuclear energy. However, the country cannot be able to switch off its power because of the high cost of power. Further, the energy requirements continue to rise almost daily and consequently, it is only through nuclear energy that currently the cities can be powered.
This paper will look at different countries nuclear power plans after the aftermath of Fukushima disaster that occurred in Japan. It will determine why different countries have decided to continue with their nuclear power plants despite the shock that came with the Fukushima disaster.
Objectives of the research study
1. To determine the reasons as to why different countries still continue to use Nuclear energy programs despite the safety concerns posed by several disasters.
2. To determine why developing countries and emerging economies are leading the race in nuclear energy programs.
3. To determine the reason as to why Germany has decided to quit its nuclear energy program despite it being cheap and sustainable.
4. Why Japan decided to return to the system of nuclear energy despite suffering one of the major disasters in modern history, regarding nuclear energy and solar energy
In conclusion, Nuclear energy has had a track record of being able to provide clean as well as reliable electricity which compares favorably when it comes to other sources of power. The near cessation of nuclear energy programs by several Western nations can be described as clearly being set back to the global energy production and degeneration. However, it is of importance to note that its effect will most likely be dwarfed in the long run by majority of the countries in the world. This is because, emerging economic giants that exist in the market such as India and China have had their nuclear plans being unabated. Despite going on a more cautious pace their development and construction of power plants cannot be seceded. After the Fukushima disaster most countries that had nuclear energy plants decided to apply brakes in order to first undertake several extensive safeties review. However, most countries still take on nuclear energy because of its cost, efficiency and reliability. Further, it does not pollute the environment. This is therefore, the main reasons as to why countries have decided that they will continue with their usual expansion in regards to nuclear power plants despite the occurrence of the Fukushima disaster.
Browse More Essay Topics 24/7/365 Support 11+ Yrs in Essay Writing Pay for Quality not Quantity Score that A+ Grade
Affordable Papers
Research Paper for Sale
Cheap Research Papers
Buy Term Papers
Buy Research Paper
Write My Paper
Buy an Essay
Cheap Essay Writer
Write my Essay
Thesis Help
Dissertation Help
Paper Writing Service
Pay for Homework
Pay for Research Paper
Do My Essay for Me
Pay for Essay
College Papers for Sale
Do My Homework for Me
College Essays for Sale
Buy Research Papers Online
Buy College paper
Client: "(Berlin, G.K., CA)"
Topic title:"Leadership shortfalls in Blue Chips"
Discipline: "Economics"
Pages: 5, (APA)
" Awesome, the writer delivered it as required by the professor. They also sent me a plagiarism & grammar report Wow!. I was worried about how the essay would turn up but this is exactly what wanted. Thank you and will be back with a longer essay"
Accounting Research Papers
Business Research Papers
Communication Research Papers
Computer Science Research Papers
Economic Research Papers
Film Studies Research Papers
Finance Research Papers
Geography Research Papers
History Essays
Psychology Research Papers
Political Science Research Papers
Nursing Research Papers
Mathematics Essays
Management Essays
Literature Essays
Law Essays
World Affairs Essays
Technology Essays
Sociology Essays
Science Essays
Religion Essays
+1(209) 348-9544
Terms
Privacy
Sitemap
Frequently Asked Questions
0% Plagiarism Guarantee
Money Back Guarantee
Revision Policy
