+1(209) 348-9544
order@myessayservices.com
+1(209) 348-9544
order@myessayservices.com
![]() Are you in High School, College, Masters, Bachelors or Ph.D and need someone to help write your essay or research? We offer premium quality essay writing help. All our papers are original, 0% plagiarized & uniquely written by our dedicated Masters specialists. My Essay Services is an experienced service with over 9 years experience in research writing of over 97,000 essays over the years. You will receive a plagiarism check certificate that confirms originality for any essay you order with My Essay Services. Fill the calculator on your right to begin placing your order now!
Are you in High School, College, Masters, Bachelors or Ph.D and need someone to help write your essay or research? We offer premium quality essay writing help. All our papers are original, 0% plagiarized & uniquely written by our dedicated Masters specialists. My Essay Services is an experienced service with over 9 years experience in research writing of over 97,000 essays over the years. You will receive a plagiarism check certificate that confirms originality for any essay you order with My Essay Services. Fill the calculator on your right to begin placing your order now!


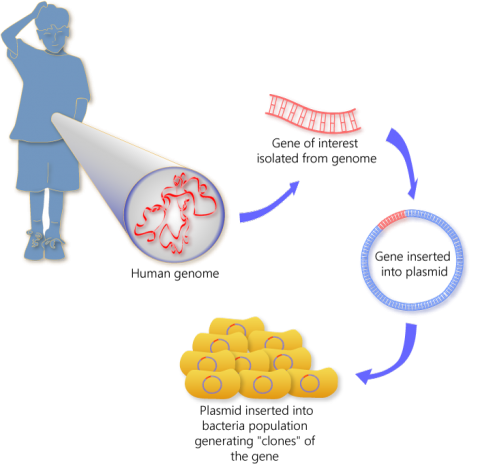 Science has been expanding for years. Today, doctors can be able to detect problems in the unborn child long before their delivery date. This has saved many lives and also made life easier for many children who would have otherwise been born with life altering conditions. However, despite this immense improvement in the standard on healthcare, several people feel that genetic enhancement and testing is interfering with the natural course of life.
Science has been expanding for years. Today, doctors can be able to detect problems in the unborn child long before their delivery date. This has saved many lives and also made life easier for many children who would have otherwise been born with life altering conditions. However, despite this immense improvement in the standard on healthcare, several people feel that genetic enhancement and testing is interfering with the natural course of life.
This is an argument based on the creation story where it is said God created everything, and everything was good. Therefore, these activists argue that medicine should not interfere with Gods intended purpose. It is my opinion that genetic testing and enhancement is a blessing to many. For instance, through genetic testing, children with problems can be diagnosed early enough for action to be taken, a factor which saves the parent and unborn child pain in the future. My support is based on the fact that everybody deserves a chance at a normal life.
Therefore, if a deformity can be avoided, why not take the necessary measure sand save the family a lot of expenses which would otherwise be spent on physical therapy and special schools, as well as the stigma associated with deformity. This paper is going to describe human cloning in relation to genetic organisms and the controversy that is as brought to the world.
Cloning is described as the genetic creation of an organism to be an identical copy of another organism through artificial means. It means that every strand of DNA in the original organism is exactly the same to its copy. The history of cloning has its roots dating back to the 1800s when plants became reproduced using cuts from stems or twigs. The cloning process has also been used in scientific experiments over the years to replicate animal cells.
The most successful breakthrough in animal cloning after 276 trials and failures came in the manner of a sheep named Dolly in 1996 (Wilmut). Many scientists led by Prof Ian Wilmut had worked tirelessly in various cloning experiments. Dolly became the first official animal clone. The cloning process has also been used on human beings. This is the artificial process of creating a genetically identical copy of an existing human being. It is also used to clone various body tissues from the individual.
In the year 1891, a German scientist known as Hans Driesch carried out a controversial experiment that led to the cloning of a sea urchin. He took the embryo of the sea urchin, shook it within a beaker filled with sea water which led to the two cells separating. He grew them separately over time and formed a separate and whole sea urchin. This scientific breakthrough disproved the claims by another biologist named August Weismann.
He believed that if embryos got separated, they would develop into two different parts of a creature. Other scientists who experimented with the cloning process and succeeded include Hans Spemann who cloned a salamander in 1902. Dr. Ian Wilmut and Dr. Keith Campbell later reproduced cloned sheep named Megan and Morag in 1986. By the year 1988, technologies used in cloning became advanced to include processes such as splitting and transfer of embryos, gene transfer and nuclear transfer (Shelton).
In the year 1993, scientists from George Washington University publicized that they had cloned human embryos. The idea was to plant them in women’s bodies during the nine months gestation period. This was never to be because the cloned cells became defective. The impressive aspect of cloning and its possibilities became officially recognized with the successful cloning of Dolly the sheep in 1996.
The fundamental purpose of this research paper is to provide an argumentative basis for and against the human cloning process. This is because the human cloning process has led to many notable achievements and also significant losses in equal measure. It has led to never-ending controversial debates over the years. There is considerable opposition to the process of copying a person. These oppositions arise from religious sectors who believe that God created the universe and cloning works against this notion. Other concerns arise from the fact that animals, which have been successfully cloned are few. In every 100 experiments, only two to three viable off springs become produced by surrogate mothers.
This shows that scientists have not been able to comprehend adequately the science involved in the animal cloning process. The scientific explanations for the successes still present loopholes. The scientists believe that these technical hurdles will one day be resolved once human cloning begins. The cloning process has opened a Pandora box regarding the ethics and morality of the process (Kolata).
The human cloning process is divided into two types called reproductive cloning which involves cloning an embryo and implanting it into a woman’s uterus. Therapeutic cloning involves cloning an embryo which is then used to generate stem cells. First of all, the human cloning process has many advantages. It led to numerous recognized advancements in scientific research. Scientists are working tirelessly to figure out ways to clone humans.
Doctors have transferred cloned embryos into women, but they did not become pregnant. The scientists believe that the procedure is not as monstrous as people made it sound (Zavos). The process has led to scientific advancements such as reproducing human stems cells through therapeutic cloning. The embryonic stem cells are grown to produce body organs and tissues used to replace the damaged ones. People suffering from burns and other ailments such as diabetes, heart diseases and damaged spinal cords may have a chance in the future to be free of the predicaments. The technology involved in human cloning could also lead to plastic surgery patients saying goodbye to cosmetic surgery procedures.
The doctors will no longer have to use silicone implants for breast augmentation or reduction. The implants sometimes leak into the bodies. They will be able to create fat, connective tissues and cartilage that match the patient’s tissues perfectly. Deformed accident victims will be able to have their limbs regenerated. Organ failures such as liver, kidney and others will be obsolete. Genetic diseases such as leukemia, cystic fibrosis and cancer will be cured.
Read also about the use of DNA as evidence in genetics
Human cloning has the advantage of improving life’s quality. This can be through the rejuvenation of the body cells. It can help in making aged people look young. According to Dr. Richard Seed, people will awaken one day to find that the aging process is reversible. This has led to slight changes in the attitudes of people towards human cloning (Merrill). The cloning process could also be used to reverse heart attacks. The doctors will clone the healthy heart cells and inject them in damaged hearts.
Heart disease is globally recognized as the number one killer in the United States and other industrialized countries. Through surveys, it is been estimated that an average human being has some eight defective genes within his body. This is what leads to the development of illnesses even with a healthy diet or exercise. With human cloning, this issue will also be a memory. The cloning technology has led to the un-matched advancement in the field of medicine. People should let go of their fears and allow the benefits to affect their lives positively. They should also be at liberty to procreate and have their freedom to reproduce. (Brock)
All things that have advantages also have their disadvantages. The human cloning process has not been left behind in this measure. Infertility has received its fair share of media coverage. The process is still unsuccessful on the infertility front. It is estimated that less than 10 percent of infertility trials are successful. The physical and psychological torture that couples undergo for the chance of having children is saddening.
The couples usually end up penniless, bankrupt, and their ticking birth clock also runs out. This might lead them to become depressed and even separation. The process has also led to many couples developing hopes that they can reproduce their baby or child lost in a car, fire or other unavoidable accidents. These parents become grief-stricken after such an event. Their hopes get shattered because of human cloning failures. This might lead them to develop mental and nervous breakdowns, which might lead to heart attacks, stroke or even death.
Security is a critical aspect for any nation and its government. The human cloning process has led to the debate of producing super humans. This could lead to the development of super-athletes or super-geniuses. People who could run faster than Usain Bolt or sharper brains than Albert Einstein. The government can also use the super-humans in their military operations against their enemies. This situation may become uncontrollable because the side-effects of producing such humans remain undetermined.
They may develop a robotic form of character that may see the loss of many lives. Their invincibility may also lead to political and social unrest. The declaration that the process could also lead to the making of a better race is also remarkably suspicious. This would lead to the discrimination of minority races in the procedures in favor of other fairly accepted races. In essence, such hypothetical fears might stem from me watching too many science fiction programs such as Face Off or Fringe.
The future aspect of using human cloning to replace body parts sends a shiver down the spine. This process might lead to the unethical murder of one human being in order to rescue another. The thought of transplanting the human brain from one body to another to prevent aging is scary. The cutting off of a body part from a healthy human being who has not given their consent is also criminal. This process might lead to identity theft. The moral rights of human beings even if they result to difficulties in research must be respected (Dworkin).
The scientists have also developed the need to play God in all aspects of life. God has provided mankind with the ability to cure diseases, fly planes and create nuclear energy. Scientists are human beings with endless goals to achieve, and human cloning is their route to their success of “Playing God”. Sometimes, one might wonder if they are playing the Devil instead. Another disadvantage is that some societies which have issues with gender.
They will use the process to clone babies from a specific gender type. It is no secret that Asian and Middle-East countries would rejoice at such progress. This is because of their discrimination against women in their societies. This is immoral and biased against the female gender. One wonders if the female gender is slowly eliminated from the gender race, who will bear the un-born children? This process could positively help in balancing out the population. The planet will be equally filled with both female and male genders in the future.
Human cloning leads to the demise of diversity as specific characteristics in human beings get selected over others. This may include strength, sharp brains, sporting talents and others. This might lead to a new race evolution with some people having great strength, but with low intelligence levels. Human life will become viewed as replaceable (Macklin). This might lead to intellectual discrimination among individuals.
The cloning process should be used as advancement in scientific research and not to take us back to the 20th century where people became slaves. The cloning procedure has also led to many embryos being at the risk of getting stolen, damaged or killed. Many embryos get created, and their viability is tested. In the process, some of them become frozen or thrown away. This has led to aggressive debates if killing a human embryo is killing a person or if it is just killing a few living cells. In a positive light, the excess embryos can be used to carry out further studies on stem research and can also be frozen until required.
In conclusion, the human cloning process should not be banned. This is because human beings are known to lack contentment in their successes. Once they achieve a goal, they want to progress further and further. There expectations are always high towards achieving success in various academic and professional fields. Human cloning can lead to some of the expectations getting fulfilled especially in medical areas such as organ replacements. The global nations have had their decent segments of success stories.
Testimonials from people who have received the treatment have also been shared. Many countries around the world should begin to accept the process as a significant life changing process. Some governments have begun to accept the possibilities of stem cell research and have invested their money in the process. The possible medical advancements to the human race might be endless. This alone should encourage governments to allow human cloning and its research. This will lead to the saving of many lives in the future. Aggressive research would also need to be carried out to establish its effectiveness on human beings and its ethical repercussions (Pollack).
Works Cited
Shelton N.J. “Embryo manipulation in research and animal production” Australian Journal of Biological Science, 1988.
Ritchie, Campbell, McWhir and Wilmut, I. “Sheep cloned by nuclear transfer from a cultured cell line” Nature, 1996.
Merril, Richard, Rose, Bryan J. “FDA Regulation of Human Cloning: Usurpation of Statesmanship.” Harvard Journal of Law and Technology, 2001.
Kolata G. “The sizzling debate about cloning human embryo” The Newyork Times, October 26, 1993.
Zavos. P. “Doctor Defends Cloning Experiment” The Associated Press, 2002.
Dworkin, R. “Taking Rights Seriously”. London: Duckworth, 1978.
Buchanan, Daniels, Wikler and Brock W.D. “From Chance to Choice: Genetics and Justice.” Cambridge University Press.2001
Pollack, R. “Beyond Cloning” New York Times, November 17, 1993.
Introduction
 In the human body, the kidneys are responsible for maintaining the balance of fluids in the body through the regulation of water balance. It is one of the respiratory organ in the human body. In addition to maintenance of water balance, the kidney plays a role of maintaining the electrolyte balance, acid-base balance and as well the excretion of the uremic toxins. Other than the excretion role played by the kidney, there is also the secretion role that the organ plays (Porth, 2009). The kidney is responsible for production of different hormones such as renin and as well activation of vitamin D3. The kidney has two regions namely cortex (outer region comprised of the glomeruli and convoluted tubes) and medulla (inner region comprised of medullary collecting tubes and blood vessels).
In the human body, the kidneys are responsible for maintaining the balance of fluids in the body through the regulation of water balance. It is one of the respiratory organ in the human body. In addition to maintenance of water balance, the kidney plays a role of maintaining the electrolyte balance, acid-base balance and as well the excretion of the uremic toxins. Other than the excretion role played by the kidney, there is also the secretion role that the organ plays (Porth, 2009). The kidney is responsible for production of different hormones such as renin and as well activation of vitamin D3. The kidney has two regions namely cortex (outer region comprised of the glomeruli and convoluted tubes) and medulla (inner region comprised of medullary collecting tubes and blood vessels).
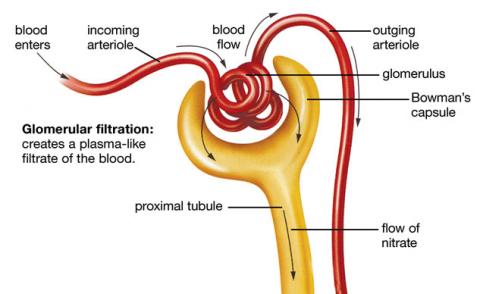
As stated earlier the kidney is an important respiratory organ in the human body. Three main processes take place in the kidney. These are glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption and tubular secretion. Glomerular filtration involves the process of ultrafiltration of the plasma in the glomerulus (Porth, 2009). This implies that as the term suggests, in the glomerulus, there are some barriers composed of fine molecular sieve that allow the filtration of small molecules. In return, there is restriction of the passage of large molecules such as blood proteins. Filtration in the glomerulus takes place because of the pressure.
Blood supplied from the renal artery flows at a high pressure and while flowing through the glomerulus, it is still at a high pressure that makes it possible for small molecules in the blood plasma to flow through the small pores in the glomerulus. On the other hand, pressure in the glomerulus originates from the arterioles supplying and leaving the Bowman’s capsule. The afferent arteriole is thicker as compared to the efferent arteriole. Implying that there is a high supply of blood to the glomerulus as compared to blood leaving the glomerulus (Porth, 2009). Large molecules in the blood plasma especially molecules having a molecular weight of 100,000 kilo Daltons are unable to pass through the walls of the glomerulus and are filtered to form the glomerular filtrate.
Similarly, plasma proteins (which are large molecules in the blood plasma) are filtered with other molecules forming the glomerular filtrate that flows to the other parts of the renal tube. There is another mechanism attributed to the process of glomerular filtration in the glomerulus. Electrical charge is another process through which glomerular filtration takes place. Barriers found in the glomerulus have a negative charge. On the other hand, most proteins found in the blood plasma have a negative charge. Therefore, it through electrostatic repulsion, there is the filtration of the negative molecules and proteins in the blood plasma (Porth, 2009).
On the other hand, tubular reabsorption refers to the process of removal of useful solutes from the glomerular filtrate returning them to the blood. Two processes takes place in during the reabsorption process. These are transcellular route (where some particles in the glomerular filtrate passes through the cytoplasm of the proximal convoluted tubule to epithelial cells and get out through their bases), the other process is paracellular route (where water passes through the joints of epithelia cells of the proximal convoluted tubule) (Porth, 2009). Through the later process, water is able to drag with it some solutes such as sodium and chlorine ions and other water-soluble substances through the process called solvent drag.
The hormone ADH is responsible for controlling water reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule. Lastly, tubular secretion as stated earlier refers to the process through which the renal tubule extracts chemicals and substances not needed in the body from the capillary blood and secretes them to the tubular fluid forming urine. Two process take place during tubular secretion. These are; waste removal and acid-base balance. Through waste removal substances such as urea, uric acid, bile acids and ammonia takes place. Waste removal is an important process during the excretion process as it clears the blood from pollutants such as aspirin and other drugs. On the other hand, acid-base balance is another important process involved during the secretion process. Through this process, there is the secretion of hydrogen and bicarbonates ions (Porth, 2009). This helps in the regulation of the body pH.
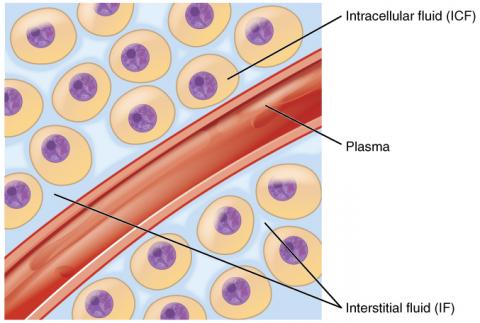 The human body comprises of two major fluids. These fluids appear mostly in the tissues. They are intracellular and extracellular fluids. Intracellular fluids are the fluids found inside the cells. on the other hand, extracellular fluid denotes all body fluids outside the cells. These fluids play a role of maintaining the osmotic pressure and potential of tissues and cells they surround. More so, they play a role of maintaining a constant pH through balancing the concentration of Hydrogen ions located in the blood plasma. Lastly, these fluids allow for the transportation of different materials through the blood and maintenance of the cells shape and turgidity.
The human body comprises of two major fluids. These fluids appear mostly in the tissues. They are intracellular and extracellular fluids. Intracellular fluids are the fluids found inside the cells. on the other hand, extracellular fluid denotes all body fluids outside the cells. These fluids play a role of maintaining the osmotic pressure and potential of tissues and cells they surround. More so, they play a role of maintaining a constant pH through balancing the concentration of Hydrogen ions located in the blood plasma. Lastly, these fluids allow for the transportation of different materials through the blood and maintenance of the cells shape and turgidity.
There lies a difference between these fluids. This is not only in their location but also in their contents and concentrations (Porth, 2009). Despite the fluids having the cell membrane separating them, they intracellular fluids have a higher concentration of potassium, phosphate and magnesium ions. This is in contrast with the extracellular fluids that have a higher concentration of sodium and chlorine ions. Lastly while the relationship between intercellular fluids and extracellular fluids, it is crucial to understand that cells are responsible for secretion of extracellular fluids. In their volumes in the human body, intercellular fluids occupy 40% of the total body weight equivalent to 25 liters. In contrast, extracellular fluids occupy 20% of body weight equivalent to 15 liters.
In their functions in the body, these fluids work in a similar manner. Movement of water between the interstitial fluid (located in the extracellular fluid) and the intercellular fluid involves a two-way osmotic flow that is equal in both directions (Porth, 2009). In addition, while maintaining the balance in osmotic pressure in the cells, ion fluxes between the extracellular fluids and intercellular fluids face a restriction. That is it happens in a two-way manner depending on the region with high concentration of ions. However, this is different with the flow of respiratory gases wastes and nutrients since their flow is in one direction.
References
Porth, C.M., & Matfin, G. (2009). Pathophysiology: Concepts of altered health states. (Eight ed.) Philadelphia, PA.
 Over the last decade, debates on the gene patenting controversy have been increasing. Scientists from different institutions are having trouble while agreeing with the controversy due to the belief of science advancements originating from free access to genes. A gene, inherited from parents to offspring, is a unit of heredity (Koepsell 96). Normally, these units determine some significant characteristic resemblances between parents and their offspring. On the other hand, patent refers to the law or license of ownership granted by the government to individuals or organizations that stops and prevents others from selling or making these products without the permission of the licensed individuals (Koepsell 102). Therefore, gene patenting refers to the controversial or giving patent rights over a discovered gene. In most situations, it grants ownership of certain DNA segments to individuals or companies. The paper objects at supporting the statement, “Gene patenting is not an intervention towards development of new medicines (Koepsell 72). As a result, allowing Gene patenting will keep new medicines from being developed. Conversely, it contributes towards limited research that will have negative effects on the overall patient care.”
Over the last decade, debates on the gene patenting controversy have been increasing. Scientists from different institutions are having trouble while agreeing with the controversy due to the belief of science advancements originating from free access to genes. A gene, inherited from parents to offspring, is a unit of heredity (Koepsell 96). Normally, these units determine some significant characteristic resemblances between parents and their offspring. On the other hand, patent refers to the law or license of ownership granted by the government to individuals or organizations that stops and prevents others from selling or making these products without the permission of the licensed individuals (Koepsell 102). Therefore, gene patenting refers to the controversial or giving patent rights over a discovered gene. In most situations, it grants ownership of certain DNA segments to individuals or companies. The paper objects at supporting the statement, “Gene patenting is not an intervention towards development of new medicines (Koepsell 72). As a result, allowing Gene patenting will keep new medicines from being developed. Conversely, it contributes towards limited research that will have negative effects on the overall patient care.”
1. Proposition
a. limits development of new medicine
Gene patenting has a strong effect on development of new medicine. Patented genes have detrimental impacts on health care innovations. Gene patenting limits scientist on the access of information related to the DNA segments. According to research carried out on the impact of gene patenting on scientist study, it revealed that about 53 percent of scientists stop doing their research due their raised concerns on the patented genes. Similarly, the published information on patented gene is drastically decreasing due to the limited access to information (Mildred 68).
Additionally, based on the limited scientific study on patent genes, the future of personalized medicine is under siege. Development of medicine results from study the by scientists. Thus, limitation of information access due to patent rights may in future crush down development of new medicine due to the weight of the gene patent thickets if the license requires scientists to scan over numerous patent holders over a single genome (Gregory 45).
b. limitation of Research
Gene patenting by itself inhibits researchers’ access to genetic information. In most situations, gene patent holders use their exclusive ownership rights to charge researchers excessive fees for genome information. Ownership of patents by one company or individual contributes to an aspect of monopoly in the medicine industry. Thus, it leads to aspects of control over utilization of specific genes for research (Crichton 37).
On the other hand, according to a recent Federal Trade Commission report, gene patenting is a contributing aspect towards decreasing biologic drugs in the modern society. Limited genetic information to researchers is inhibiting their success towards developing new and alternative cures to diseases presented on patients. Some gene-related disorders require active research aimed at understanding the change in DNA segments. Conversely, limited access to these genomes often limits other individuals from trying to develop new treatments to diseases (Mildred 33).
c. It hurts overall patient care
Despite the intensive negative impacts experienced by researchers and scientists on gene patenting, patient health care as well experiences limitation due to these exclusive rights. Genes are facts of nature. Therefore, they are not patentable (Gregory 59). Patenting of genes limits patient’s access to life-saving genetic diagnosis tests. Similarly, the monopolistic nature of these tests leads to increased prices. Conversely, it limits patient’s access to health care. Gene licensing does not offer patients with second-opinion tests for confirming the tests provided by their doctors (Koepsell 45).
While treating and responding to some disorders, it is important to understand the patient’s DNA segmentations. Therefore, it requires active collective of genetic information from patients. Disorders such cancer require continuous innovations and research. However, under gene patenting rights, the overall studying process is cumbersome. Thus, response to these disorders is entirely hurting to patient’s health (Crichton 27).
d. limited gene commercial activities
Patent rights contribute to individual ownership of gene segments. Thus, the use of patented isolated human DNA segments requires permissions from these owners. In addition, performing patent methods and tests as well require confirmation. Thus, profit-oriented tests and use of DNA faces limitation. There is a strong interpretation of gene patenting as a legitimate commercial regulation activity (Calfee 66).
2. Opposition
Despite the opposed approach on gene patenting, the licensing as well presents some advantages to in the healthcare industry. After the enacting laws gene patenting rights, basic research on BRCA1 and BRCA2 had significantly increased. Despite the patenting of these genes, public gene database reveals that a high number of scientists pursue their research on these genes aimed at developing the NA segments and their representation. After development of the patenting rights, research on these genes became formal. Similarly, it concludes that gene patenting does not cripple genetic research (Crichton 77).
Surprisingly, gene licensing promotes internal research. Thus, patent right owners have the capability of pursuing their research and thus able to develop more precise cures on these drugs. In addition, unlike in the other case where there is a strong negative impact on the development of new treatment, increased research on patent owners facilitate innovation of new treatment procedures and medicines (Gregory 102). Lastly, knowledge advancement is another advantage attributed to gene patenting. Where licensed organizations and individuals engage in continuous researches, there are chances of gaining further knowledge from these tests.
Concessions
The University of Utah, a patent owner on BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, provides a notation that lab research does not experience negative impacts from gene patenting. Their database presents an increased research on these genes. More so, National Academy of Sciences study showed that there is little evidence on hemming up of research labs by Gene Patents. Nevertheless, Ethics Illustrated journal reveals a strong stand against gene patenting revealing its negative impacts on innovation and patient health (Calfee 52).
Development of the argument
The research began after a telephone survey carried out on United States laboratory directors between July and September in 2001. The study targeted members of the Association for Molecular Pathology. The study entailed interviewing of one hundred thirty-two of 211 (63%) laboratory directors. The study did not include ten of the directors since they did not conduct DNA-based genetic tests. Almost all performed genetic tests for clinical purposes. Half of the sample population performed tests for research purposes as well. The study revealed that twenty-eight of the respondents stopped performing their tests test due to the gene patent rights. More so, seventy respondents reported that their decisions of failure of developing new clinical genetic test resulted from the patents. The study as well revealed that some laboratories faced a limitation towards carrying out of some tests. According to a response developed from the directors, approximately 22 patents had a relevance towards the limited tests. Conclusively, the study revealed that patents have strong negative impacts on the cost of tests and access to genetic information (Calfee 32).
Conclusion
In conclusion, as seen in the discussion above, it is true that gene patenting is not an intervention towards development of new medicines. As a result, allowing Gene patenting will keep new medicines from being developed. Conversely, it contributes towards limited research that will have negative effects on the overall patient care. Its role in inhibiting innovations, development of new medicine, and hurting patient care leads to the conclusive negative approach towards gene patenting.
Reference
Calfee, E. John. “Decoding the Use of Gene Patents.” Perspectives on Contemporary Issues: Reading Across the Disciplines. 7th edition, Ed. Katherine Anne Ackley, CT: Cengage Learning, 2014. 343-45. Print
Crichton, Michael. “Patenting Life.” Perspectives on Contemporary Issues: Reading Across the Disciplines. 7th edition, Ed. Katherine Anne Ackley, CT: Cengage Learning, 2014. 441-43. Print
Gregory, Anthony. “Why legalizing Organ Sales Would Help To Safe Lives, End Violence.” Perspectives on Contemporary Issues: Reading Across the Disciplines. 7th edition, Ed.4Katherine Anne Ackley, CT: Cengage Learning, 2014. 351-53. Print
Effects of Patents and Licenses on the Provision of Clinical Genetic Testing Services Cho, Mildred K. et al. The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics , Volume 5 , Issue 1 , 3-8
Koepsell, David. Who Owns You: The Corporate Gold Rush to Patent Your Genes. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2011. Internet resource.
Jones, Phill. Stem Cell Research and Other Cell-Related Controversies. New York: Infobase Pub, 2011. Internet resource.
Browse More Essay Topics 24/7/365 Support 11+ Yrs in Essay Writing Pay for Quality not Quantity Score that A+ Grade
Affordable Papers
Research Paper for Sale
Cheap Research Papers
Buy Term Papers
Buy Research Paper
Write My Paper
Buy an Essay
Cheap Essay Writer
Write my Essay
Thesis Help
Dissertation Help
Paper Writing Service
Pay for Homework
Pay for Research Paper
Do My Essay for Me
Pay for Essay
College Papers for Sale
Do My Homework for Me
College Essays for Sale
Buy Research Papers Online
Buy College paper
Client: "(Berlin, G.K., CA)"
Topic title:"Leadership shortfalls in Blue Chips"
Discipline: "Economics"
Pages: 5, (APA)
" Awesome, the writer delivered it as required by the professor. They also sent me a plagiarism & grammar report Wow!. I was worried about how the essay would turn up but this is exactly what wanted. Thank you and will be back with a longer essay"
Accounting Research Papers
Business Research Papers
Communication Research Papers
Computer Science Research Papers
Economic Research Papers
Film Studies Research Papers
Finance Research Papers
Geography Research Papers
History Essays
Psychology Research Papers
Political Science Research Papers
Nursing Research Papers
Mathematics Essays
Management Essays
Literature Essays
Law Essays
World Affairs Essays
Technology Essays
Sociology Essays
Science Essays
Religion Essays
+1(209) 348-9544
Terms
Privacy
Sitemap
Frequently Asked Questions
0% Plagiarism Guarantee
Money Back Guarantee
Revision Policy
